What is ERP in company – Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a game-changer for businesses, revolutionizing the way they operate and optimize their resources. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of ERP, exploring its definition, components, benefits, challenges, and more.
From streamlining processes to empowering decision-making, ERP offers a wealth of opportunities for businesses of all sizes. Let’s embark on this journey to unravel the intricacies of ERP and discover how it can transform your organization.
Components of an ERP System
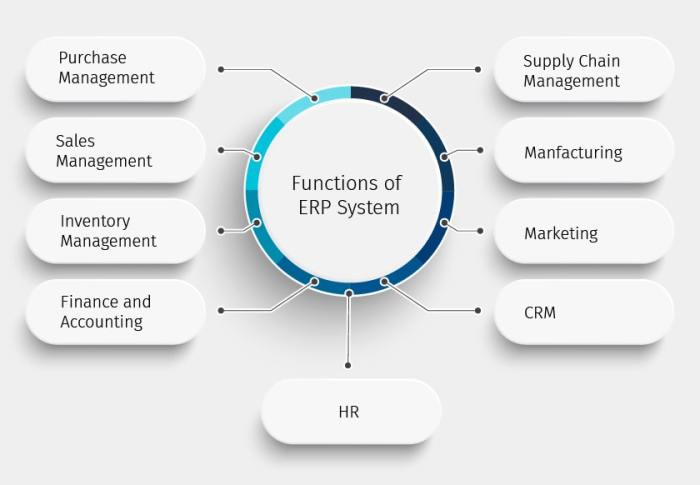
ERP systems comprise various interconnected modules that work together to manage an organization’s business processes. These modules provide a comprehensive view of the organization’s operations, enabling efficient data sharing and seamless communication across departments.
Core Components
The core components of an ERP system typically include:
- Financial Management:Handles accounting, budgeting, cash flow management, and financial reporting.
- Supply Chain Management:Manages the flow of goods and services, from procurement to delivery.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):Tracks customer interactions, manages sales pipelines, and provides customer support.
- Human Capital Management (HCM):Automates HR processes, including payroll, benefits administration, and talent management.
- Project Management:Provides tools for planning, executing, and tracking projects.
Additional Modules
In addition to the core components, ERP systems often include additional modules tailored to specific industry requirements, such as:
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES):Monitors and controls production processes in real-time.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM):Manages the entire lifecycle of a product, from design to disposal.
- Business Intelligence (BI):Provides data analysis and reporting tools for informed decision-making.
These components work together to provide a holistic view of an organization’s operations, enabling businesses to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and gain competitive advantage.
Challenges of ERP Implementation
ERP implementation can be a daunting task for businesses, as it involves integrating various aspects of an organization into a single system. This process can be complex and time-consuming, and there are several challenges that businesses may encounter along the way.
Some of the most common challenges associated with ERP implementation include:
- Data integration:Integrating data from multiple sources can be a complex and time-consuming process. This is especially true for businesses that have legacy systems that are not compatible with the new ERP system.
- Cost:ERP systems can be expensive to purchase and implement. This includes the cost of the software itself, as well as the cost of consulting, training, and support.
- Time:ERP implementations can take a long time to complete. This is especially true for businesses that have complex operations or a large number of employees.
- Change management:ERP implementation can require significant changes to the way a business operates. This can be difficult for employees to adjust to, and it can lead to resistance to the new system.
- Risk:ERP implementations can be risky. If the implementation is not successful, it can disrupt the business’s operations and lead to financial losses.
To mitigate these challenges, businesses should carefully plan and execute their ERP implementations. This includes:
- Developing a clear implementation plan:This plan should Artikel the scope of the implementation, the timeline, and the budget.
- Selecting the right ERP system:The ERP system should be a good fit for the business’s needs and should be compatible with its existing systems.
- Engaging a qualified implementation partner:An experienced implementation partner can help the business to plan and execute the implementation successfully.
- Communicating with employees:The business should communicate with employees about the ERP implementation and its benefits. This will help to reduce resistance to the new system.
- Training employees:Employees should be trained on the new ERP system before it is implemented. This will help them to learn how to use the system effectively.
- Testing the system:The ERP system should be tested thoroughly before it is implemented. This will help to identify and fix any bugs.
- Monitoring the implementation:The business should monitor the ERP implementation closely to ensure that it is on track and that it is meeting the business’s needs.
ERP Selection Process

Selecting the right ERP system for your company is a critical decision. The wrong choice can lead to wasted time, money, and resources. That’s why it’s important to follow a thorough selection process.
The ERP selection process typically involves the following steps:
- Define your business requirements.
- Create a vendor shortlist.
- Request demos from vendors.
- Evaluate vendor proposals.
- Make a decision.
Factors to Consider When Evaluating Vendors
When evaluating different ERP vendors, there are a number of factors to consider, including:
- Functionality
- Cost
- Scalability
- Implementation time
- Vendor support
It’s also important to consider your company’s specific needs and goals. For example, if you’re a small business, you may not need a full-featured ERP system. Instead, you may be able to get by with a more affordable and easier-to-implement solution.
Importance of a Thorough Selection Process, What is ERP in company
Taking the time to carefully select an ERP system is essential for ensuring that you get the best possible solution for your business. A thorough selection process will help you:
- Avoid costly mistakes.
- Get the most out of your ERP investment.
- Improve your business processes.
By following the ERP selection process and considering the factors discussed above, you can increase your chances of selecting the right ERP system for your company.
ERP Implementation Process
ERP implementation is a complex process that involves multiple phases, stakeholders, and timelines. Understanding these aspects is crucial for successful implementation.The ERP implementation process typically consists of the following phases:
Project Initiation
- Define project scope, objectives, and timeline.
- Establish a project team and assign roles and responsibilities.
- Conduct a feasibility study to assess readiness and potential benefits.
Business Process Analysis
- Document and analyze existing business processes.
- Identify areas for improvement and optimization.
- Develop a roadmap for aligning business processes with the ERP system.
Software Selection
- Evaluate different ERP vendors and solutions.
- Conduct vendor demonstrations and site visits.
- Select the most suitable ERP software based on requirements and budget.
Implementation
- Configure and customize the ERP system to fit business needs.
- Integrate the ERP system with other systems and applications.
- Train users on the new system and processes.
Testing and Go-Live
- Conduct thorough testing to ensure system accuracy and functionality.
- Resolve any issues identified during testing.
- Prepare for and execute the go-live transition to the new ERP system.
Post-Implementation
- Monitor system performance and user adoption.
- Provide ongoing support and maintenance.
- Continuously evaluate and optimize the ERP system to meet evolving business needs.
Roles and Responsibilities of Stakeholders
Various stakeholders play key roles in the ERP implementation process:
- Project Sponsor:Provides executive leadership and support.
- Project Manager:Manages the overall project and ensures timely delivery.
- Business Process Owners:Define and optimize business processes.
- IT Team:Implements and integrates the ERP system.
- End Users:Utilize the ERP system for daily operations.
ERP Implementation Timeline
The timeline for ERP implementation can vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization. However, a typical implementation can take anywhere from 6 months to 2 years, with the following milestones:
- Project Initiation:1-3 months
- Business Process Analysis:3-6 months
- Software Selection:3-6 months
- Implementation:6-12 months
- Testing and Go-Live:3-6 months
- Post-Implementation:Ongoing
Post-Implementation Support
The successful implementation of an ERP system is just the beginning of the journey. Ongoing support is crucial to ensure that the system continues to meet the evolving needs of the organization. Post-implementation support encompasses a range of services designed to maintain, enhance, and troubleshoot the ERP system.
There are several types of post-implementation support available, including:
- Technical support:Resolving technical issues, providing system updates, and ensuring optimal performance.
- Functional support:Assisting users with system functionality, training, and process optimization.
- Customization support:Modifying the ERP system to meet specific business requirements and integrations.
- Regulatory compliance support:Ensuring that the ERP system meets industry regulations and standards.
To ensure a successful post-implementation phase, organizations should consider the following tips:
- Establish a dedicated support team:A team responsible for managing post-implementation support, including technical experts, functional analysts, and business users.
- Define clear support processes:Documenting support procedures, escalation paths, and response times to ensure efficient issue resolution.
- Provide ongoing training:Regularly training users on system updates, new features, and best practices to maximize system utilization.
- Monitor system performance:Regularly reviewing system metrics, such as uptime, response times, and user satisfaction, to identify areas for improvement.
- Continuously evaluate and improve:Regularly gathering feedback from users and conducting system audits to identify areas for enhancement and optimization.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can ensure that their ERP system remains a valuable asset, supporting their business operations and driving ongoing success.
ERP Trends and Innovations
ERP technology is constantly evolving, driven by the need to meet the changing demands of businesses. Modern ERP systems offer a wide range of new features and capabilities that can help organizations improve their efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. Some of the most important trends in ERP technology include:
- Cloud computing:Cloud-based ERP systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their flexibility, scalability, and affordability. Cloud ERP systems can be accessed from anywhere, making it easy for employees to collaborate and share data.
- Artificial intelligence (AI):AI is being used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. AI-powered ERP systems can help organizations identify trends, predict outcomes, and make better decisions.
- Machine learning:Machine learning is a type of AI that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning algorithms can be used to improve the accuracy of forecasting, identify fraud, and optimize supply chains.
- Data analytics:ERP systems are increasingly being used to collect and analyze data. This data can be used to improve decision-making, identify trends, and optimize business processes.
- Mobility:ERP systems are becoming increasingly mobile, allowing employees to access data and perform tasks from anywhere. Mobile ERP systems can help organizations improve their productivity and flexibility.
These are just a few of the trends that are shaping the future of ERP technology. As ERP systems continue to evolve, they will become even more essential for businesses of all sizes.
Impact of AI and Cloud Computing on ERP
AI and cloud computing are two of the most important technologies that are driving the evolution of ERP systems. AI can be used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. Cloud computing makes it possible to access ERP systems from anywhere, making it easy for employees to collaborate and share data.The combination of AI and cloud computing is creating new possibilities for ERP systems.
For example, AI-powered ERP systems can be used to:
- Identify trends:AI algorithms can be used to identify trends in data, which can help organizations make better decisions.
- Predict outcomes:AI algorithms can be used to predict outcomes, such as the likelihood of a customer churning or the demand for a particular product.
- Optimize supply chains:AI algorithms can be used to optimize supply chains, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Detect fraud:AI algorithms can be used to detect fraud, such as fraudulent transactions or insurance claims.
- Personalize customer experiences:AI algorithms can be used to personalize customer experiences, such as by recommending products or services that are tailored to their individual needs.
Cloud computing is also having a major impact on ERP systems. Cloud-based ERP systems are more flexible, scalable, and affordable than on-premises ERP systems. Cloud ERP systems can be accessed from anywhere, making it easy for employees to collaborate and share data.The combination of AI and cloud computing is creating new possibilities for ERP systems.
As these technologies continue to evolve, ERP systems will become even more essential for businesses of all sizes.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software system that integrates various business processes into a single platform. It streamlines operations by providing a centralized view of data and automating tasks. For small businesses, choosing between CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and ERP can be challenging.
While CRM focuses on managing customer interactions, ERP offers a comprehensive solution that encompasses finance, inventory, and supply chain management. To determine the best fit, businesses should consider their specific needs and resources. Learn more about the key differences between CRM and ERP to make an informed decision.
ERP for Small Businesses: What Is ERP In Company
Small businesses face unique challenges in managing their operations efficiently. ERP systems can offer a comprehensive solution to streamline processes, improve collaboration, and gain valuable insights. However, selecting and implementing ERP systems for small businesses requires careful consideration.
Benefits of ERP for Small Businesses
* Streamlined Operations:ERP systems integrate various business functions into a single platform, reducing manual tasks and improving efficiency.
Improved Collaboration
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software that integrates various business processes within a company. It helps companies manage their operations more efficiently. Similar to ERP, CRM ( What is CRM ) is a software that helps companies manage their customer relationships.
By integrating CRM with ERP, companies can gain a better understanding of their customers and improve their overall customer experience. This can lead to increased sales and improved customer satisfaction.
ERP systems provide a central repository for data, allowing different departments to access and share information seamlessly.
Increased Productivity
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a software solution that integrates various business processes into a single platform. It provides a comprehensive view of a company’s operations, from finance and accounting to supply chain management and customer relationship management (CRM). To understand the advantages of ERP, it’s worth comparing it with CRM.
CRM focuses on managing customer interactions , while ERP encompasses a broader range of business functions. By integrating these systems, companies can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions that drive growth.
Automated processes and real-time data visibility help employees work more efficiently and make better decisions.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate various business processes into a single platform, streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. By connecting ERP with artificial intelligence (AI)-powered customer relationship management (CRM) tools, companies can further optimize customer interactions. Leveraging AI in CRM enables personalized marketing, proactive support, and data-driven decision-making, ultimately transforming customer relationships and driving business growth.
ERP systems play a crucial role in this integration, providing real-time data and insights to enhance CRM functionality and drive organizational success.
Enhanced Reporting and Analytics
ERP systems generate comprehensive reports and provide insights into key performance indicators, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Improved Customer Service
ERP systems provide a 360-degree view of customer interactions, enabling businesses to respond promptly and effectively.
Challenges of ERP for Small Businesses
* Cost:ERP systems can be expensive to purchase and implement, especially for small businesses with limited budgets.
Complexity
ERP systems can be complex to implement and require significant technical expertise.
Time
Implementing an ERP system can be a time-consuming process that requires careful planning and execution.
Data Migration
Migrating data from legacy systems to an ERP system can be challenging and may lead to data loss or errors.
Resistance to Change
Employees may resist the implementation of an ERP system, fearing job displacement or disruption of their workflows.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a crucial software that integrates various business functions into a single system. It streamlines processes and improves efficiency. In the dynamic business landscape, staying ahead requires adopting the latest trends. CRM Trends to Watch in 2024: Staying Ahead in a Competitive Market provides insights into the emerging CRM technologies that can enhance customer relationships and drive growth.
By leveraging ERP and staying abreast of CRM advancements, companies can optimize their operations and gain a competitive edge.
Considerations for Small Businesses
* Identify Business Needs:Determine the specific business challenges that an ERP system can address.
Choose a Scalable Solution
Select an ERP system that can grow with the business as it expands.
Consider Cloud-Based Options
Cloud-based ERP systems offer flexibility, reduced upfront costs, and automatic updates.
Seek Professional Support
Partner with an experienced ERP implementation consultant to guide the process and minimize risks.
Provide Training and Support
Ensure that employees are adequately trained on the ERP system and receive ongoing support.
ERP Selection and Implementation for Small Businesses
* Evaluate Vendor Options:Research and compare different ERP vendors to find the best fit for the business’s needs.
Conduct a Pilot Implementation
Implement the ERP system in a limited area to test its functionality and identify any potential issues.
Plan for Data Migration
Develop a comprehensive data migration plan to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
Manage Change
Communicate the benefits of the ERP system to employees and provide training to minimize resistance.
Monitor and Evaluate
Regularly review the performance of the ERP system and make adjustments as needed.
Last Word
In conclusion, ERP is a transformative tool that empowers businesses to achieve operational excellence. By integrating disparate systems and providing real-time data, ERP enables organizations to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge. As technology continues to evolve, ERP will undoubtedly remain a cornerstone of modern business operations, driving innovation and shaping the future of enterprise management.
FAQs
What is the primary purpose of an ERP system?
ERP systems are designed to integrate and streamline all core business processes, providing a single, centralized platform for managing operations.
What are the key components of an ERP system?
ERP systems typically include modules for finance, supply chain management, human resources, manufacturing, and customer relationship management.
What are the potential benefits of implementing an ERP system?
ERP systems can improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance decision-making, and provide real-time visibility into business operations.





