As The Ultimate Guide to Defining ERP SAP for Business Optimization takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. ERP SAP stands as a transformative force in the business landscape, and this guide delves into its intricacies, empowering organizations to harness its full potential for unparalleled optimization and growth.
Within these pages, we embark on a comprehensive exploration of ERP SAP, deciphering its core components, unraveling its benefits, and illuminating the industries and functions that stand to gain from its transformative power. Together, we navigate the intricacies of planning and implementation, ensuring a seamless transition that unlocks the true potential of this enterprise resource planning solution.
Introduction
ERP SAP is a powerful tool that can help businesses of all sizes optimize their operations. By integrating all of your business data into a single system, ERP SAP can help you improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make better decisions.This guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of ERP SAP, including its benefits, features, and implementation process.
We will also discuss some of the challenges that you may face when implementing ERP SAP, and how to overcome them.
Key Concepts
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
As we navigate the complexities of ERP SAP for business optimization, it’s crucial to delve into the nuances of selecting the right ERP solution. To that end, I highly recommend exploring How to Choose the Right erps Truck Stop.
This comprehensive guide will empower you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and ensure your ERP implementation aligns seamlessly with your business objectives.
A software system that integrates all of a business’s data into a single system.
SAP(Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing)
A leading provider of ERP software.
The Ultimate Guide to Defining ERP SAP for Business Optimization delves into the intricacies of ERP systems, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in streamlining business processes. For a broader perspective on ERP’s impact, refer to ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency.
This resource explores the fundamentals of ERP, highlighting its benefits for enhancing collaboration, efficiency, and overall business performance. By combining these insights, The Ultimate Guide to Defining ERP SAP for Business Optimization empowers you with the knowledge to leverage ERP systems effectively, driving innovation and success in your organization.
Business Optimization
The Ultimate Guide to Defining ERP SAP for Business Optimization provides a comprehensive overview of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, including SAP. For a deeper understanding of the differences between ERP and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, refer to ERP vs.
CRM: A Comprehensive Guide to Unraveling the Key Differences. This guide will help you gain insights into the functionalities, benefits, and implementation considerations of both ERP and CRM systems, enabling you to make informed decisions for your business optimization.
The process of improving a business’s efficiency and profitability.
Understanding ERP SAP
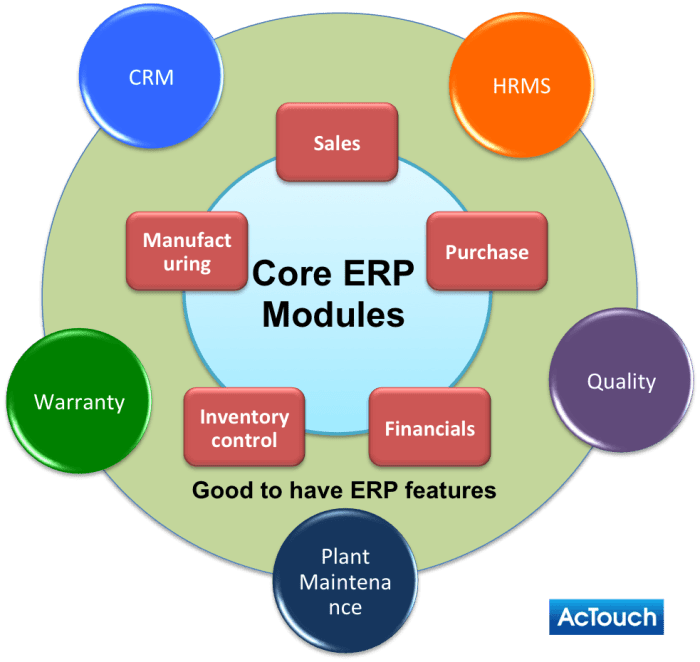
ERP SAP, or Enterprise Resource Planning SAP, is a comprehensive software suite designed to integrate and streamline various business processes within an organization. It offers a central platform that connects departments, functions, and data, enabling businesses to gain real-time visibility, improve efficiency, and optimize operations.ERP SAP comprises several core components, including:
Financial Management
Manages financial transactions, accounting, and reporting.
Human Capital Management
Automates HR processes, including payroll, benefits, and talent management.
Supply Chain Management
Optimizes inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics.
Customer Relationship Management
Tracks customer interactions, sales, and marketing activities.
Business Intelligence
Provides data analytics and reporting capabilities for informed decision-making.Implementing ERP SAP offers numerous benefits for businesses, including:
Increased Efficiency
Automates processes, reduces manual tasks, and improves workflow.
Enhanced Collaboration
Breaks down silos between departments, facilitating seamless communication and coordination.
Real-Time Visibility
Provides access to up-to-date data, allowing businesses to monitor operations and make timely decisions.
Improved Decision-Making
Offers data analytics and reporting tools that support informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Reduced Costs
Streamlines processes, eliminates redundancies, and improves resource utilization.ERP SAP is particularly beneficial for industries such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and professional services. It can also enhance business functions like accounting, finance, supply chain management, human resources, and customer service.
If you’re looking for a deep dive into ERP SAP and how it can revolutionize your business, check out The Ultimate Guide to Defining ERP SAP for Business Optimization. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about ERP SAP, from its benefits to its implementation.
But if you’re just starting out with ERP/MRP systems, I recommend reading ERP/MRP Systems: The Key to Unlocking Business Efficiency first. This article provides a solid foundation in the basics of ERP/MRP systems and how they can help you streamline your business processes.
Once you’ve read that, you’ll be ready to dive into the details of ERP SAP and how it can take your business to the next level.
Planning and Implementation
ERP SAP implementation is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Key steps include:
- Business Process Analysis:Document current processes, identify areas for improvement, and define future state requirements.
- Software Selection:Evaluate and select the ERP SAP module that best meets business needs.
- Data Migration:Convert and transfer existing data into the new ERP SAP system.
- Configuration:Customize the ERP SAP system to align with specific business requirements.
- Testing:Conduct thorough testing to ensure the system functions as expected.
- Go-Live:Deploy the ERP SAP system and train users on the new processes.
Timeline and Resource Allocation
A typical ERP SAP implementation timeline ranges from 12 to 18 months, depending on the size and complexity of the organization. Resource allocation should consider the following:
- Project Team: Business analysts, IT specialists, and end-users.
- Budget: Hardware, software, implementation services, and training.
- Change Management: Communication, training, and support for users during the transition.
Change Management Best Practices
Effective change management is crucial for successful ERP SAP implementation. Best practices include:
- Communication:Keep stakeholders informed about the project progress and benefits.
- Training:Provide comprehensive training to users on the new system and processes.
- Resistance Management:Address user concerns and provide support to minimize resistance.
- Phased Approach:Implement the system in phases to reduce disruption and allow for gradual adoption.
- Post-Implementation Support:Offer ongoing support to users after go-live to ensure a smooth transition.
Customization and Integration
Customizing ERP SAP is essential to tailor it to specific business needs, optimizing its functionality and efficiency. Integration with other systems further enhances its capabilities, enabling seamless data flow and streamlined operations.
Importance of Customization
- Improved efficiency:Customization automates tasks and streamlines processes, saving time and resources.
- Enhanced functionality:Adding specific features and modules extends ERP SAP’s capabilities, meeting unique business requirements.
- Increased user adoption:A customized system is tailored to users’ needs, improving adoption and reducing resistance to change.
Integration Options
ERP SAP can be integrated with various systems, including:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):Integrates customer data and interactions for improved customer service.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM):Connects ERP SAP with suppliers and logistics providers, optimizing inventory management and order fulfillment.
- Business Intelligence (BI):Enables data analysis and reporting, providing insights for better decision-making.
Benefits of Integration, The Ultimate Guide to Defining ERP SAP for Business Optimization
- Centralized data:Integration eliminates data silos, ensuring data consistency and accessibility across systems.
- Improved collaboration:Sharing data among systems enhances collaboration between departments and teams.
- Increased efficiency:Automated data flow reduces manual errors and streamlines processes.
Examples of Successful Customization and Integration
Many businesses have successfully customized and integrated ERP SAP to achieve significant benefits, including:
- Nike:Customized ERP SAP to streamline its global supply chain, reducing lead times and improving customer satisfaction.
- Coca-Cola:Integrated ERP SAP with its CRM system to gain a 360-degree view of customers, leading to personalized marketing campaigns.
Data Management and Security

Data management and security are crucial for the successful implementation and operation of ERP SAP. ERP SAP stores and processes vast amounts of sensitive data, including financial information, customer data, and operational details. Effective data management ensures the accuracy, integrity, and accessibility of this data, while robust security measures protect it from unauthorized access, theft, or damage.
Data Governance Strategies
Data governance establishes policies and procedures for managing data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to storage, use, and disposal. Key strategies include:
- Defining data ownership and responsibilities
- Establishing data quality standards
- Implementing data lineage and audit trails
- Enforcing data retention and disposal policies
Security Measures and Compliance
ERP SAP offers a comprehensive set of security measures, including:
- User authentication and authorization
- Data encryption
- Audit logging and intrusion detection
- Firewall and network security
Compliance with industry regulations and standards is essential, such as:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
- ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System)
By implementing sound data management and security practices, organizations can ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of their critical data within ERP SAP, mitigating risks and safeguarding business operations.
Business Process Optimization: The Ultimate Guide To Defining ERP SAP For Business Optimization
ERP SAP offers a comprehensive suite of tools and functionalities that enable businesses to streamline and optimize their key business processes. By integrating various aspects of an organization’s operations into a single, centralized platform, ERP SAP helps eliminate redundancies, improve communication, and enhance overall efficiency.
ERP SAP’s workflow automation capabilities allow businesses to automate repetitive tasks, such as order processing, inventory management, and financial transactions. This automation not only saves time and resources but also reduces the risk of errors and improves accuracy.
Case Study: Process Optimization in Manufacturing
- A manufacturing company implemented ERP SAP to streamline its production processes. The system integrated inventory management, production planning, and quality control modules, providing real-time visibility into the entire production cycle.
- The company was able to reduce lead times by 20% and improve product quality by 15% through enhanced coordination and data sharing.
Reporting and Analytics
ERP SAP’s reporting and analytics capabilities empower businesses with valuable insights into their operations. Through comprehensive dashboards and reports, businesses can monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track trends, and identify areas for improvement.
These data-driven insights enable informed decision-making, allowing businesses to optimize processes, reduce costs, and increase profitability. ERP SAP’s advanced analytics tools facilitate data exploration and visualization, providing real-time insights into various business aspects.
Dashboards and Reports
ERP SAP offers a wide range of customizable dashboards and reports that cater to specific business needs. These include:
- Financial dashboards:Provide real-time insights into financial performance, including revenue, expenses, and profitability.
- Operational dashboards:Monitor key metrics related to production, inventory, and supply chain management.
- Sales dashboards:Track sales performance, customer trends, and opportunities.
- Human capital management reports:Provide insights into employee performance, attendance, and compensation.
Cloud-Based ERP SAP
Cloud-based ERP SAP is a cloud-based solution that provides businesses with a centralized platform to manage their operations. It offers a number of benefits, including:
- Reduced costs: Cloud-based ERP SAP is typically less expensive than on-premise solutions, as businesses do not need to invest in hardware and infrastructure.
- Increased flexibility: Cloud-based ERP SAP is more flexible than on-premise solutions, as businesses can scale their usage up or down as needed.
- Improved collaboration: Cloud-based ERP SAP enables businesses to collaborate more effectively, as users can access the system from anywhere with an internet connection.
Comparison of Cloud-Based ERP SAP to On-Premise Solutions
Cloud-based ERP SAP and on-premise ERP SAP are two different types of ERP solutions. Cloud-based ERP SAP is hosted by a third-party provider, while on-premise ERP SAP is hosted on the business’s own servers.There are a number of key differences between cloud-based ERP SAP and on-premise ERP SAP, including:
- Cost: Cloud-based ERP SAP is typically less expensive than on-premise ERP SAP, as businesses do not need to invest in hardware and infrastructure.
- Flexibility: Cloud-based ERP SAP is more flexible than on-premise ERP SAP, as businesses can scale their usage up or down as needed.
- Security: Cloud-based ERP SAP is typically more secure than on-premise ERP SAP, as third-party providers have a vested interest in protecting their customers’ data.
Future Trends and Implications of Cloud-Based ERP SAP
Cloud-based ERP SAP is a growing trend, as businesses increasingly recognize the benefits of cloud computing. In the future, cloud-based ERP SAP is likely to become even more popular, as businesses continue to adopt cloud-based solutions.The implications of cloud-based ERP SAP for businesses are significant.
Cloud-based ERP SAP can help businesses to reduce costs, increase flexibility, and improve collaboration. As a result, cloud-based ERP SAP is likely to play an increasingly important role in the future of business.
Vendor Selection and Evaluation
Selecting the right vendor is crucial for a successful ERP SAP implementation. This section guides businesses through the vendor selection process, provides criteria for evaluating vendors, and shares insights on vendor contracts and negotiations.
Vendor Selection Process
- Define business requirements and project goals.
- Research and identify potential vendors.
- Request proposals and evaluate responses.
- Conduct reference checks and site visits.
- Negotiate and finalize the vendor contract.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
Evaluate vendors based on the following criteria:
- Industry expertise:Experience and understanding of your business sector.
- Product capabilities:Functionality, scalability, and alignment with business needs.
- Implementation experience:Proven track record and successful ERP SAP projects.
- Support and maintenance:Level of support provided, response times, and service agreements.
- Cost and pricing:Total cost of ownership, including licensing, implementation, and maintenance.
Vendor Contracts and Negotiations
Negotiate a vendor contract that clearly defines:
- Scope of work and deliverables.
- Timeline and milestones.
- Payment terms and conditions.
- Intellectual property rights.
- Warranties and guarantees.
Return on Investment (ROI)
ERP SAP implementations can deliver significant ROI, enhancing operational efficiency, streamlining processes, and driving business growth. Measuring ROI involves quantifying the benefits against the implementation costs.
Financial Benefits
* Reduced costs:Automating processes, consolidating systems, and eliminating redundancies can significantly reduce operational expenses.
Increased revenue
Improved data visibility, enhanced customer relationship management (CRM), and supply chain optimization can boost sales and profitability.
Improved cash flow
Automated billing and payment processing can accelerate cash flow and reduce accounts receivable days.
Operational Benefits
* Enhanced efficiency:Streamlined workflows, automated tasks, and real-time data access improve productivity and reduce errors.
Increased agility
ERP SAP provides a flexible platform to adapt to changing business needs, enabling rapid response to market demands.
To truly grasp the significance of ERP SAP for business optimization, refer to ERP: Unlocking the Power of Integrated Business Management. This comprehensive guide will illuminate how ERP SAP seamlessly connects various business functions, streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency.
By leveraging this invaluable resource, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how ERP SAP can transform your business into a cohesive and thriving enterprise.
Improved customer satisfaction
Integrated CRM and support modules enhance customer interactions, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Case Studies
* A manufacturing company reported a 20% reduction in production costs and a 15% increase in sales revenue after implementing ERP SAP.
A healthcare organization experienced a 30% decrease in patient wait times and a 10% increase in patient satisfaction scores.
Case Studies and Success Stories
In the realm of business optimization, ERP SAP implementations have proven to be transformative for organizations across industries. Real-world case studies showcase the tangible benefits and challenges encountered during these implementations, providing valuable insights into the strategies used to overcome them.
From streamlining operations to enhancing data visibility, ERP SAP has empowered businesses to achieve significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. Success stories from companies that have leveraged ERP SAP to drive growth and innovation serve as compelling evidence of its transformative potential.
Case Study: Global Manufacturing Company
- Challenge:Streamlining disparate systems and improving supply chain visibility
- Strategy:Implemented ERP SAP to integrate inventory management, production planning, and logistics
- Result:Reduced lead times by 20%, improved inventory accuracy by 15%, and enhanced customer satisfaction
Testimonial: CEO of a Healthcare Provider
“ERP SAP has transformed our operations, enabling us to provide seamless patient care while optimizing our resources. We have witnessed a significant reduction in administrative costs and improved collaboration among our healthcare teams.”
Closing Summary
As we reach the culmination of this guide, a profound realization emerges: ERP SAP is not merely a software solution; it is a catalyst for business transformation. By embracing its capabilities, organizations can streamline operations, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market landscape.
This guide serves as a beacon, illuminating the path towards ERP SAP mastery and empowering businesses to achieve unprecedented heights of success.
FAQ Section
What is ERP SAP?
ERP SAP is an enterprise resource planning (ERP) software solution designed to integrate and streamline various business processes, providing a centralized platform for data management and operational efficiency.
What are the benefits of implementing ERP SAP?
ERP SAP offers numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy, enhanced collaboration, increased productivity, reduced costs, and better decision-making capabilities.
What industries can benefit from ERP SAP?
ERP SAP is applicable across a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, retail, healthcare, education, and non-profit organizations.
How do I choose the right ERP SAP vendor?
Selecting the right ERP SAP vendor involves evaluating their experience, industry expertise, customer support, and alignment with your business goals.
How can I measure the return on investment (ROI) of ERP SAP?
ROI can be measured by assessing improvements in operational efficiency, cost savings, increased revenue, and enhanced customer satisfaction.





