The maximum loan limit is calculated from salary, and this relationship is crucial for understanding your borrowing power. Whether you’re planning to buy a home, finance a car, or consolidate debt, your salary plays a significant role in determining how much you can borrow.
In this article, we’ll explore the intricate relationship between salary and loan limits, examining how your income influences your loan eligibility and the factors considered in calculating your maximum borrowing capacity. We’ll also delve into alternative income sources, exceptions to salary-based loan limits, and the ethical implications of using salary as a primary factor in loan approvals.
Loan Limit Calculation Methods
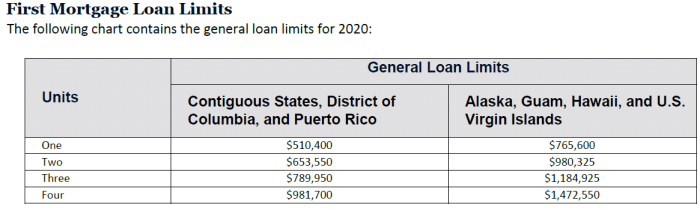
The maximum loan limit is typically calculated based on a percentage of the borrower’s salary. The exact formula used may vary depending on the lender and the type of loan being applied for.
Some of the most common loan limit calculation methods include:
Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI)
The DTI ratio is a measure of how much of the borrower’s monthly income is already being used to pay off debt. Lenders typically want to see a DTI ratio of 36% or less before approving a loan. To calculate the DTI ratio, add up all of the borrower’s monthly debt payments, including rent or mortgage, car payments, student loans, and credit card payments.
Then divide that number by the borrower’s monthly gross income.
Remember to click kendaraan bermotor to understand more comprehensive aspects of the kendaraan bermotor topic.
Front-End Ratio, The maximum loan limit is calculated from salary
The front-end ratio is a measure of how much of the borrower’s monthly income is being used to pay for housing costs. Lenders typically want to see a front-end ratio of 28% or less before approving a loan. To calculate the front-end ratio, divide the borrower’s monthly housing costs by their monthly gross income.
Investigate the pros of accepting coin coin crypto in your business strategies.
Back-End Ratio
The back-end ratio is a measure of how much of the borrower’s monthly income is being used to pay for all debt, including housing costs. Lenders typically want to see a back-end ratio of 36% or less before approving a loan.
Discover the crucial elements that make coin crypto the top choice.
To calculate the back-end ratio, add up all of the borrower’s monthly debt payments, including housing costs, and divide that number by the borrower’s monthly gross income.
Income Verification for Loan Applications
Verifying income is a crucial step in the loan application process. It helps lenders assess the borrower’s ability to repay the loan and manage their finances. The process involves several steps and the examination of various documents to ensure the accuracy of the income information provided.
Salary Documentation
Salary documentation is a primary source of income verification. It provides evidence of the borrower’s regular income, including wages, salaries, bonuses, and commissions. Lenders typically require the following documents for salary verification:
- Recent pay stubs (covering at least the past two to three months)
- Employment verification letter from the employer
- W-2 forms (for the past two years)
Loan Limit Sensitivity to Salary Changes
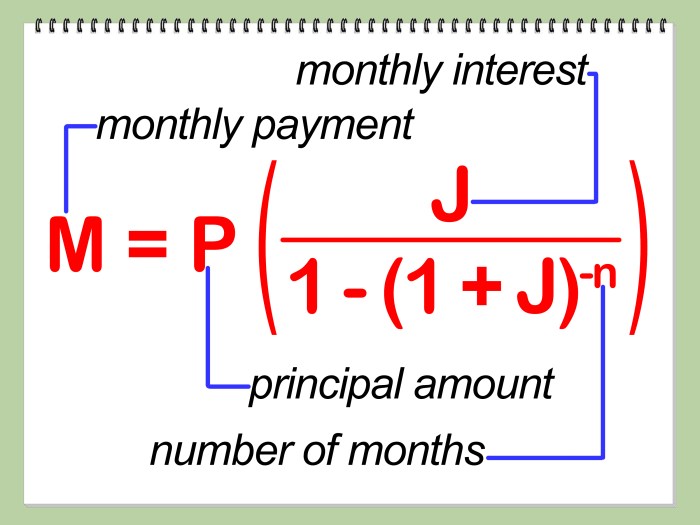
Loan limits are directly tied to an individual’s salary. As salary fluctuates, so too does the maximum loan amount they qualify for. Understanding this sensitivity is crucial for both lenders and borrowers.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out mobil bekas now.
When a salary increases, the loan limit typically increases proportionally. This is because lenders use salary as a key indicator of an individual’s ability to repay the loan. A higher salary means a greater capacity to make loan payments on time and in full.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of jualbeli rumah.
Conversely, when a salary decreases, the loan limit may also decrease. Lenders need to ensure that the borrower can still afford the loan payments even with the reduced income. A sudden or significant decrease in salary could make it difficult for the borrower to meet their financial obligations.
Scenarios
Let’s illustrate this sensitivity with a few scenarios:
- Scenario 1:An individual with a salary of $50,000 qualifies for a loan limit of $200,000. If their salary increases to $60,000, their loan limit may increase to $240,000.
- Scenario 2:An individual with a salary of $40,000 qualifies for a loan limit of $160,000. If their salary decreases to $30,000, their loan limit may decrease to $120,000.
These scenarios highlight the importance of considering salary changes when determining loan eligibility. Both lenders and borrowers should be aware of how fluctuations in income can impact the loan limit.
End of Discussion
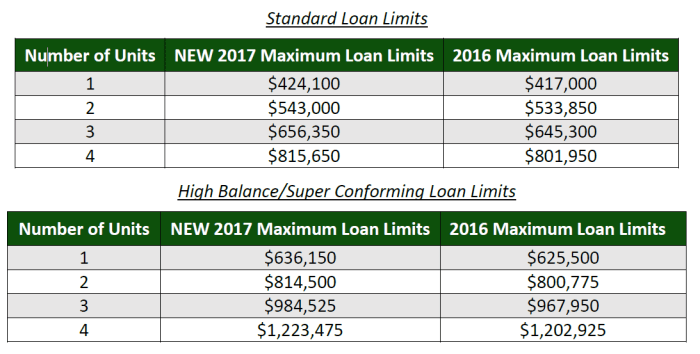
Understanding the relationship between salary and loan limits empowers you to make informed financial decisions. By carefully considering your income, expenses, and financial goals, you can determine the appropriate loan amount for your circumstances and maximize your chances of loan approval.
Remember, responsible borrowing is essential for financial well-being, and it all starts with understanding the factors that influence your loan limit.
Clarifying Questions: The Maximum Loan Limit Is Calculated From Salary
How does my salary affect my loan limit?
Your salary is a key factor in determining your loan limit because it provides lenders with an indication of your ability to repay the loan. A higher salary generally translates to a higher loan limit.
What other factors are considered in calculating my loan limit?
In addition to your salary, lenders also consider your debt-to-income ratio, credit history, and employment stability when calculating your loan limit.
Can I get a loan if my salary is low?
Yes, it is possible to get a loan even if your salary is low. However, you may need to explore alternative loan options, such as secured loans or loans from non-traditional lenders.





