Embark on a journey into the future of Ethereum with Eth2 and Comparison. This comprehensive analysis delves into the transformative features and advancements that set Eth2 apart, unraveling the key differences between Ethereum 1.0 and its successor. Prepare to witness a captivating exploration of consensus mechanisms, scalability enhancements, and security measures that redefine the Ethereum landscape.
As we delve into the heart of Eth2, we’ll uncover the significance of the shift from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake, exploring the implications for network security and energy consumption. We’ll unravel the concept of sharding, shedding light on its role in boosting transaction throughput and scalability.
Moreover, we’ll examine the importance of data availability, exploring the role of data availability committees in safeguarding network integrity.
Introduction to Eth2: Eth2 And Comparison
Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2) is a major upgrade to the Ethereum blockchain that aims to address the network’s scalability and sustainability issues. It introduces a number of key features and improvements, including:
Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism
Eth2 replaces the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work mechanism with a more efficient Proof-of-Stake mechanism. This reduces the computational power required to validate transactions and secure the network.
Sharding
Eth2 divides the Ethereum blockchain into 64 smaller, more manageable shards. This allows for parallel transaction processing, significantly increasing the network’s throughput.
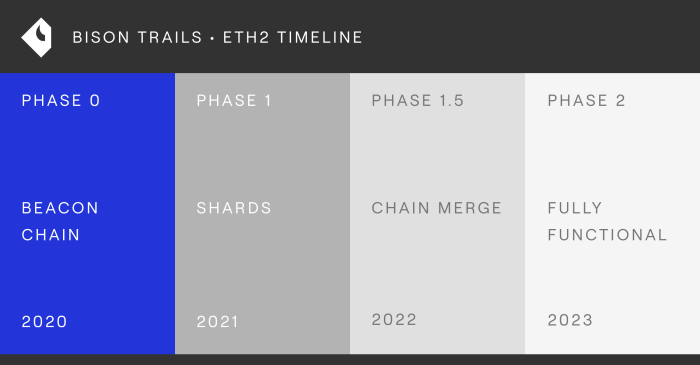
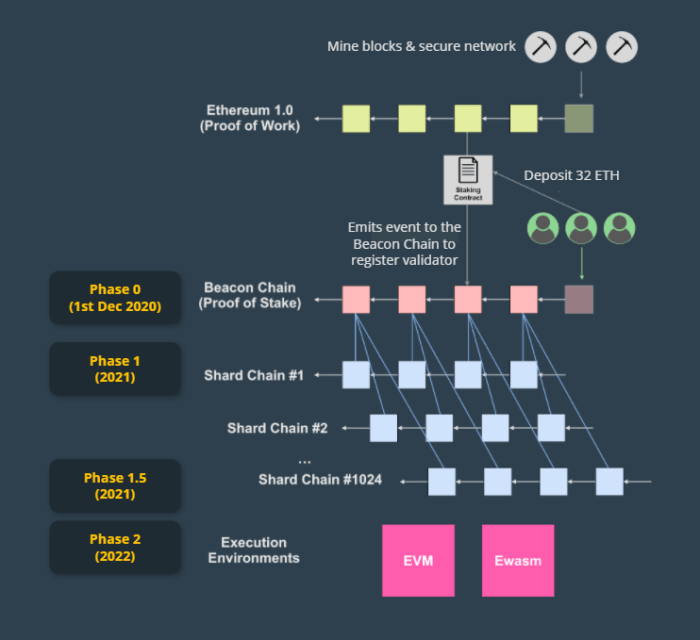
Beacon Chain
The Beacon Chain is a new blockchain that coordinates the validators and manages the state of the shards. It also introduces a new token called ETH2, which is used for staking and rewards.
Merge
The Merge is the process of combining the existing Ethereum blockchain with the Beacon Chain. This will create a single, more efficient blockchain that incorporates all of the features of Eth2.
Comparison of Eth1 and Eth2
Ethereum 1.0 (Eth1) and Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2) are two distinct versions of the Ethereum blockchain, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Here’s a comparison of the key differences between the two:
Consensus Mechanism
Eth1 uses a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This process is energy-intensive and can be slow and expensive.
Eth2, on the other hand, uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. In PoS, validators stake their ETH to participate in the consensus process. Validators are randomly selected to propose and validate new blocks, and they earn rewards for their participation.
Transaction Processing
Eth1 uses a single-chain architecture, which means that all transactions are processed sequentially on the main blockchain. This can lead to congestion and slow transaction times, especially during periods of high demand.
Eth2 introduces sharding, which splits the blockchain into multiple parallel chains called shards. Each shard processes its own set of transactions, which helps to increase the overall throughput and scalability of the network.
Scalability, Eth2 and comparison
Eth1 is limited in its scalability due to the limitations of the PoW consensus mechanism and the single-chain architecture. Eth2, with its PoS consensus mechanism and sharding, is designed to be much more scalable than Eth1, allowing it to handle a higher volume of transactions and support a wider range of applications.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are the backbone of any blockchain network, ensuring that all participants agree on the validity of transactions and the state of the network. In the transition from Eth1 to Eth2, there is a significant shift in the consensus mechanism used, from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
PoW, as used in Eth1, requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This process is energy-intensive and can lead to centralization, as miners with more computing power have a higher chance of earning rewards.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
PoS, on the other hand, is a more energy-efficient and equitable consensus mechanism. In PoS, validators are chosen based on the amount of ETH they stake. Validators then take turns proposing and validating new blocks, and they are rewarded for their participation.
Eth2, the highly anticipated upgrade to Ethereum, is still under development and its comparison with other platforms is ongoing. While we wait for the dust to settle, let’s take a break and explore a nifty feature that can make your messaging experience a breeze.
WhatsApp Chat Search allows you to quickly find specific conversations, saving you precious time. Once you’re done catching up, you can return to the fascinating world of eth2 and its evolving landscape.
The benefits of PoS include:
- Energy efficiency:PoS consumes significantly less energy compared to PoW.
- Reduced centralization:PoS makes it more difficult for a single entity to control the network, as validators are chosen based on their stake rather than their computing power.
- Increased scalability:PoS is more scalable than PoW, as it does not require validators to solve complex mathematical puzzles.
However, PoS also has some drawbacks:
- Security concerns:PoS can be vulnerable to attacks if a majority of validators collude.
- Initial investment:To become a validator in a PoS network, users need to stake a significant amount of ETH.
- Rewards distribution:Validators with larger stakes receive a higher proportion of rewards, which can lead to wealth inequality.
Sharding
Sharding is a technique used in Eth2 to improve scalability and transaction throughput. It involves dividing the Ethereum blockchain into smaller, more manageable pieces called shards.
Each shard is responsible for processing a subset of transactions and maintaining a portion of the blockchain data. This allows for parallel processing, where multiple shards can work simultaneously on different transactions, significantly increasing the overall capacity of the network.
Shard Chains
Shards in Eth2 are represented by shard chains. Each shard chain has its own set of validators, responsible for verifying and adding new blocks to the chain. Transactions are randomly assigned to different shard chains, ensuring an even distribution of workload.
With eth2’s promise of faster transactions and lower fees, it’s worth considering its potential impact on the crypto landscape. However, staying organized amidst the influx of digital communication can be a challenge. Discover how to master WhatsApp archive management with our guide: Master WhatsApp Archive Management: A Breezy Guide to Keep Your Chats in Check . This will help you declutter your chats while ensuring essential messages remain accessible.
Returning to the topic of eth2 and comparison, it’s crucial to evaluate its features against existing solutions to make informed decisions.
Cross-Shard Transactions
While shards operate independently, there may be instances where transactions need to interact across different shards. To facilitate this, Eth2 introduces cross-shard transactions.
The highly anticipated Ethereum 2.0 (Eth2) is a significant upgrade to the Ethereum blockchain, promising increased scalability and efficiency. While Eth2 is still under development, its potential impact on the crypto world is already being compared to other major blockchain advancements.
In the meantime, why not revamp your WhatsApp chats with stylish themes to keep your conversations fresh and visually appealing? Revamp Your WhatsApp Chats with Stylish Themes offers a variety of options to personalize your chat experience, adding a touch of style to your Eth2 discussions.
Cross-shard transactions are routed through a special contract called the Crosslink. The Crosslink ensures that transactions are securely transferred between shards and that the integrity of the overall blockchain is maintained.
Data Availability
Data availability is crucial in Eth2 because it ensures that all validators have access to the same set of data, which is necessary for them to reach consensus on the state of the network. Without data availability, validators could be misled by malicious actors into believing that a different version of the blockchain is valid, which could lead to a split in the network.
Data availability is ensured by data availability committees (DACs). DACs are groups of validators that are responsible for storing and serving data from the blockchain. When a validator requests data from a DAC, the DAC must provide the data within a certain amount of time.
If a DAC fails to provide the data, the validator can punish the DAC by slashing its stake.
DACs and Network Security
DACs play an important role in network security by ensuring that validators have access to the same set of data. This makes it more difficult for malicious actors to attack the network by misleading validators into believing that a different version of the blockchain is valid.
Additionally, the slashing mechanism ensures that DACs are incentivized to provide data in a timely manner.
Virtual Machine
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a core component of Eth2 that enables the execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It serves as a sandboxed environment where code can run securely and deterministically across the Ethereum network.The EVM in Eth2 has undergone significant enhancements compared to Eth1.
It features a stack-based architecture with a 256-bit word size and a set of opcodes that define the operations that can be performed. The EVM is designed to be Turing-complete, allowing developers to create complex and sophisticated smart contracts.
In the realm of cryptocurrency, the buzz surrounding Eth2 and its potential for transforming the Ethereum network continues to dominate conversations. As developers and enthusiasts delve into the intricacies of its upgrades, it’s equally important to stay abreast of other advancements that enhance our digital experiences.
One such innovation is WhatsApp Video, which has revolutionized the way we share visual content with loved ones and colleagues. WhatsApp Video: The Ultimate Guide to Sharing Like a Pro provides invaluable tips and tricks to elevate your WhatsApp video-sharing game.
By mastering these techniques, you can seamlessly integrate the latest advancements into your digital interactions, while continuing to follow the exciting developments in Eth2 and its implications for the future of blockchain technology.
Smart Contracts and dApp Development
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They operate on the EVM and are stored on the Ethereum blockchain. Smart contracts enable the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) that run on the Ethereum network.dApps
While we delve into the intricacies of eth2 and its implications for the future of blockchain technology, it’s equally important to master the art of captivating storytelling. Take a moment to explore Master WhatsApp Story Posting Essentials: The Ultimate Guide to Captivating Your Audience . By understanding the nuances of storytelling in the digital age, you’ll enhance your ability to engage your audience and make your content truly memorable.
As we continue our exploration of eth2 and its potential impact, remember that effective communication is paramount for driving adoption and fostering a vibrant community.
leverage smart contracts to facilitate a wide range of applications, including decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), and more. The EVM provides a platform for developers to build and deploy these dApps, fostering innovation and growth within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees on Ethereum have become a major concern for users, especially during periods of high network congestion. In Eth1, transaction fees are determined by a combination of factors, including the complexity of the transaction, the size of the transaction, and the current network congestion.
This can lead to significant variability in transaction fees, making it difficult for users to predict how much they will need to pay.Eth2 aims to reduce transaction costs and improve affordability through several key changes. First, Eth2 introduces a new fee structure that is designed to be more predictable and transparent.
Under this new structure, transaction fees will be determined by a base fee and a priority fee. The base fee is set by the network and will be used to cover the cost of processing the transaction. The priority fee is set by the user and will be used to incentivize miners to process the transaction more quickly.
This new fee structure will give users more control over the cost of their transactions and will help to reduce the variability in transaction fees.Second, Eth2 will introduce sharding, which will help to distribute the load on the network and reduce congestion.
This will help to reduce the overall cost of processing transactions and will make it possible to process more transactions at a lower cost.Third, Eth2 will introduce a new data availability layer that will help to ensure that all transactions are available to all nodes on the network.
This will help to reduce the risk of censorship and will make it more difficult for miners to manipulate the network.Overall, Eth2’s new fee structure, sharding, and data availability layer are all designed to reduce transaction costs and improve affordability.
These changes will make Ethereum more accessible to users and will help to support the growth of the Ethereum ecosystem.
Scalability
Ethereum 2.0 introduces significant scalability enhancements to address the limitations of Ethereum 1.0. These enhancements enable the network to process more transactions, reduce latency, and support a growing number of users and applications.
One of the key scalability improvements in Eth2 is sharding, which involves dividing the network into multiple parallel chains, or shards. Each shard operates independently, processing its own set of transactions. This parallelization allows the network to handle a much higher volume of transactions simultaneously.
Transaction Capacity
With sharding, Eth2 is expected to achieve a significant increase in transaction capacity compared to Eth1. The exact capacity will depend on the number of shards implemented, but estimates suggest that Eth2 could process tens of thousands of transactions per second (TPS), compared to the current limit of around 15 TPS on Eth1.
Latency Reduction
In addition to increased transaction capacity, Eth2 also aims to reduce latency, or the time it takes for a transaction to be confirmed. By distributing the workload across multiple shards, Eth2 can process transactions more efficiently, leading to faster confirmation times.
Scalability Benefits
The scalability enhancements in Eth2 will bring several benefits to the Ethereum ecosystem, including:
- Support for more users and applications:Increased transaction capacity and reduced latency will enable Ethereum to support a larger number of users and a wider range of applications.
- Reduced transaction fees:With higher transaction capacity, the cost of sending transactions on Ethereum is expected to decrease, making it more affordable for users.
- Improved user experience:Faster confirmation times and lower transaction fees will improve the user experience for Ethereum applications.
Security
Eth2’s security is bolstered by a trifecta of enhancements: Proof-of-Stake (PoS), sharding, and data availability.
PoS introduces economic incentives to ensure validator honesty, making it prohibitively expensive to attack the network. Sharding further strengthens security by distributing the network across multiple shards, reducing the impact of any single point of failure.
Data Availability
Data availability plays a crucial role in maintaining network integrity. Each shard contains a subset of the blockchain data, and validators are responsible for ensuring that this data is accessible to all participants. This distributed data storage makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to tamper with the network’s history.
Final Thoughts

In the concluding chapter of our Eth2 and Comparison odyssey, we’ll delve into the practical implications of these advancements. We’ll analyze the impact of reduced transaction costs on user affordability and the broader Ethereum ecosystem. We’ll also assess the scalability enhancements, providing concrete examples of increased transaction capacity and reduced latency.
Finally, we’ll scrutinize the security measures implemented in Eth2, highlighting how PoS, sharding, and data availability collectively contribute to a more robust and resilient network.
FAQ Insights
What is the primary purpose of Ethereum 2.0?
Eth2 aims to enhance Ethereum’s scalability, security, and energy efficiency, laying the foundation for widespread adoption and real-world applications.
How does Eth2 improve scalability?
Eth2 introduces sharding, a technique that divides the network into smaller, more manageable partitions, enabling parallel transaction processing and significantly increasing throughput.
What is the significance of the Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism in Eth2?
PoS replaces the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work mechanism, reducing the environmental impact and potentially improving network security by incentivizing validators to act honestly.





