Prepare to dive into the world of ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency. This comprehensive exploration will unravel the intricacies of ERP, empowering you to harness its transformative potential for seamless operations and remarkable growth.
ERP, an acronym for Enterprise Resource Planning, stands as a robust business software solution designed to streamline your organization’s core processes. Imagine a symphony of interconnected modules, each dedicated to a crucial aspect of your business, from finance and supply chain to human resources.
By integrating ERP into your operations, you embark on a journey towards enhanced efficiency, reduced costs, and unparalleled decision-making capabilities.
ERP Meaning and Definition
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It is a software solution that integrates various business processes into a single system. This allows businesses to manage their operations more efficiently and effectively.
ERP as a Business Software Solution
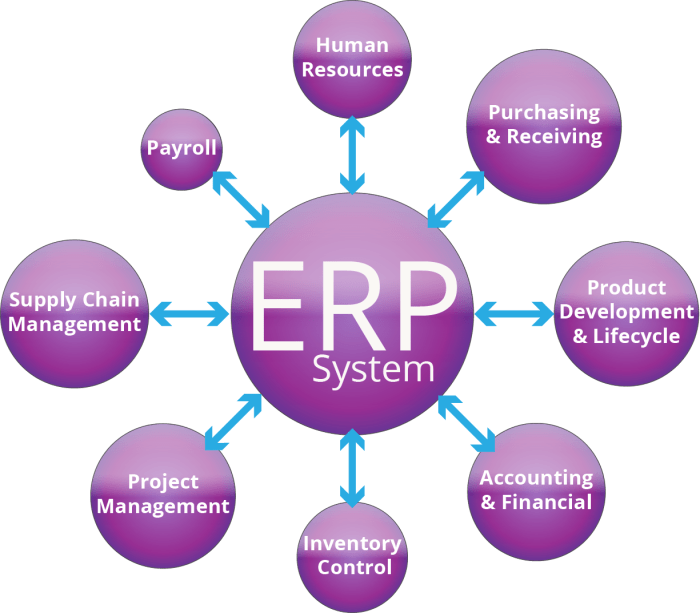
ERP systems are designed to provide a comprehensive view of a business’s operations. They typically include modules for:
- Financial management
- Human resources management
- Supply chain management
- Customer relationship management
- Manufacturing
- Project management
By integrating these modules into a single system, ERP systems can help businesses to:
- Improve communication and collaboration between departments
- Reduce costs by eliminating duplicate data entry and streamlining processes
- Increase efficiency by automating tasks and providing real-time data
- Gain a competitive advantage by leveraging data to make better decisions
Benefits of ERP Integration
ERP integration offers a myriad of advantages for businesses seeking to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. By centralizing and automating various business processes, ERP systems eliminate redundant tasks, improve data accuracy, and facilitate real-time decision-making.
Enhanced Data Management
ERP systems provide a single, centralized repository for all business data, including customer information, inventory levels, and financial transactions. This eliminates the need for maintaining multiple spreadsheets or databases, reducing the risk of data inconsistencies and errors. Real-time data access allows for faster and more accurate reporting, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
Improved Process Efficiency
ERP systems automate many manual tasks, such as order processing, inventory management, and financial reporting. This frees up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives and reduces the likelihood of human error. By streamlining processes, businesses can significantly reduce lead times and improve overall operational efficiency.
ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency covers the fundamentals of enterprise resource planning (ERP). To illustrate these concepts, ERP System Example: The Ultimate Guide to Transforming Your Business provides real-world examples of how ERP can transform organizations.
Returning to the core principles, ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency explores the benefits and challenges of implementing ERP systems, providing valuable insights for businesses seeking to enhance their efficiency and integration.
Increased Collaboration and Communication, ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency
ERP systems provide a platform for seamless collaboration and communication across different departments within an organization. Real-time data sharing and visibility enable teams to work together more effectively, eliminating bottlenecks and improving coordination. This fosters a culture of transparency and accountability, enhancing decision-making and driving business growth.
Better Customer Service
ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of customer interactions, allowing businesses to track customer preferences, purchase history, and support requests. This information empowers customer service representatives to resolve issues quickly and efficiently, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Reduced Costs
ERP integration can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By automating tasks, reducing errors, and improving efficiency, businesses can reduce labor costs, inventory waste, and operational expenses. Additionally, ERP systems provide real-time insights into business performance, enabling businesses to identify areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation.
ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning, is a business management software that integrates all aspects of a company’s operations. It can help businesses improve efficiency, productivity, and customer service. Similarly, Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) Therapy is a type of cognitive behavioral therapy that can help people overcome anxiety disorders.
ERP Therapy works by gradually exposing people to the things they fear and teaching them how to cope with their anxiety. By using ERP, businesses and individuals can improve their performance and well-being.
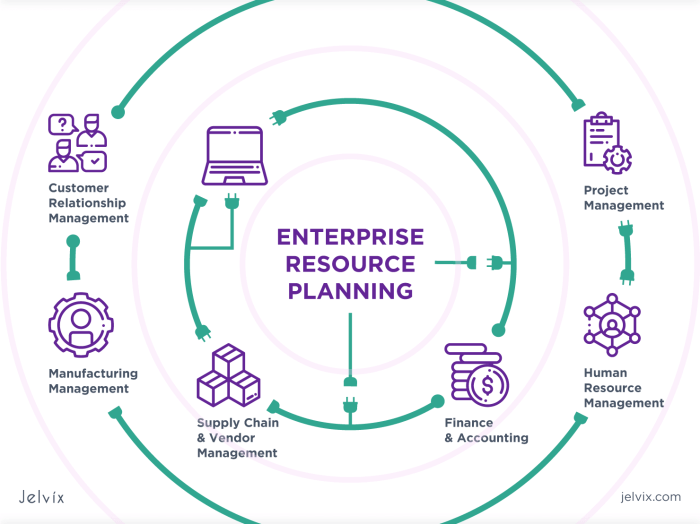
Key Modules of an ERP System

ERP systems consist of several core modules that work together to streamline business processes and provide a comprehensive view of the organization. These modules cover various functional areas, including finance, supply chain management, human resources, and more.
Finance Module
The finance module is responsible for managing the financial aspects of an organization, including accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting. It helps businesses track income and expenses, manage cash flow, and ensure compliance with financial regulations. The finance module provides real-time financial data and insights, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and improve financial performance.
Supply Chain Management Module
The supply chain management module optimizes the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. It includes functions such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics. By integrating data from different stages of the supply chain, businesses can improve inventory visibility, reduce lead times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Human Resources Module
The human resources module manages employee-related data and processes, such as payroll, benefits, and performance management. It provides a central repository for employee information, automates HR tasks, and streamlines communication between HR and employees. The human resources module helps businesses attract, retain, and develop a skilled workforce.
ERP Implementation Considerations
ERP implementation requires careful planning and execution to ensure successful integration. Key factors to consider include:
- Data migration:Transferring data from legacy systems to the ERP is crucial for seamless integration. Data should be cleansed, standardized, and validated to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Process mapping:Analyzing and documenting existing business processes helps identify inefficiencies and optimize them for the new ERP system. This ensures smooth transitions and minimizes disruptions.
- User training:Employees need comprehensive training to understand the ERP system and maximize its functionality. This empowers them to leverage the system effectively and drive business improvements.
Project Management
ERP implementation is a complex project that requires effective project management to ensure timely delivery, budget adherence, and stakeholder satisfaction. Key aspects include:
- Project plan:A detailed plan Artikels project scope, timeline, resources, and communication channels to guide implementation.
- Stakeholder management:Identifying and engaging stakeholders throughout the project ensures buy-in and minimizes resistance to change.
- Risk management:Anticipating and mitigating potential risks helps minimize disruptions and ensures project success.
ERP Selection Process
ERP selection is a critical process for businesses seeking to implement an integrated software solution. It involves evaluating various vendors and solutions to determine the best fit for the organization’s specific needs.
The ERP selection process typically involves the following steps:
- Define business requirements: Identify the business processes, pain points, and goals that the ERP system should address.
- Research potential vendors: Conduct research to identify vendors that offer ERP solutions that align with the business requirements.
- Request for proposals (RFP): Issue an RFP to shortlisted vendors outlining the business requirements and evaluation criteria.
- Evaluate vendor responses: Review vendor responses to the RFP and assess their solutions based on functionality, scalability, cost, and other criteria.
- Conduct demos and proof of concepts (POCs): Request demos and POCs from the top vendors to evaluate the user interface, performance, and integration capabilities of their solutions.
- Negotiate and select the vendor: Negotiate contract terms with the selected vendor and finalize the implementation plan.
Criteria for Evaluating Potential Vendors and Solutions
When evaluating potential ERP vendors and solutions, it is important to consider the following criteria:
- Functionality:Ensure that the solution meets the specific business requirements and provides the necessary functionality.
- Scalability:Consider the organization’s current and future growth plans and select a solution that can scale to meet increasing demands.
- Cost:Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including license fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance.
- Vendor reputation and support:Research the vendor’s track record, industry expertise, and customer support capabilities.
- Implementation time and complexity:Assess the estimated implementation time and complexity, and ensure that the organization has the resources to support the project.
- Integration capabilities:Determine how easily the ERP solution can integrate with existing systems and applications.
Cloud vs. On-Premise ERP: ERP Meaning And Definition: The Ultimate Guide To Business Integration And Efficiency
Cloud-based and on-premise ERP solutions offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, catering to different organizational needs and preferences. Cloud ERP is hosted by a third-party provider and accessed over the internet, while on-premise ERP is installed and managed on the organization’s own servers.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Cloud and On-Premise ERP
Organizations should consider several factors when selecting between cloud and on-premise ERP solutions, including:
Cost
Cloud ERP typically has lower upfront costs but may involve ongoing subscription fees, while on-premise ERP requires significant initial investment in hardware, software, and IT staff.
Flexibility
Cloud ERP offers greater flexibility and scalability, allowing organizations to easily adjust their system to changing needs, while on-premise ERP requires more complex and time-consuming upgrades.
Security
Both cloud and on-premise ERP solutions can provide robust security measures, but organizations should carefully evaluate the security protocols of each provider.
Control
On-premise ERP provides organizations with greater control over their data and system, while cloud ERP involves relying on a third-party provider.
IT Resources
Cloud ERP eliminates the need for organizations to maintain their own IT infrastructure, while on-premise ERP requires dedicated IT staff for maintenance and support.
ERP Integration Challenges
ERP integration can be a complex and challenging process for businesses. Potential challenges include:
- Data integration:Combining data from multiple sources into a single ERP system can be complex and time-consuming.
- Process changes:Implementing an ERP system often requires businesses to change their existing processes, which can be disruptive and difficult to manage.
- Cost:ERP systems can be expensive to purchase and implement, and ongoing maintenance and support costs can be significant.
- Technical complexity:ERP systems are complex software solutions that require specialized knowledge and expertise to implement and maintain.
- Resistance to change:Employees may resist changes to their existing processes and workflows, which can slow down the ERP implementation process.
Overcoming ERP Integration Challenges
To overcome these challenges, businesses should:
- Plan carefully:Develop a detailed implementation plan that addresses all aspects of the ERP integration process.
- Get buy-in from stakeholders:Involve key stakeholders in the planning and implementation process to ensure their support.
- Choose the right ERP vendor:Select an ERP vendor that has experience in your industry and can provide the support you need.
- Implement in phases:Break the ERP implementation process down into smaller, more manageable phases.
- Train employees thoroughly:Provide employees with comprehensive training on the new ERP system.
- Monitor progress and make adjustments:Track the progress of the ERP implementation and make adjustments as needed.
By following these strategies, businesses can increase their chances of successfully integrating an ERP system and achieving the benefits it can offer.
ERP Trends and Innovations
The ERP industry is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These advancements are shaping the future of ERP solutions, making them more powerful, flexible, and user-friendly than ever before.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is the backbone of business integration and efficiency, providing a comprehensive overview of your operations. For small businesses looking to scale up, Unlock Growth with ERP for Small Businesses: The Ultimate Guide offers a step-by-step roadmap.
This guide empowers you to leverage ERP to streamline processes, improve decision-making, and drive growth. Return to our ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency for a deeper dive into the concepts and benefits of ERP.
One of the most significant trends in the ERP industry is the move towards cloud-based solutions. Cloud ERP systems are hosted on a remote server, which means that businesses can access them from anywhere with an internet connection. This makes them a great option for businesses that have multiple locations or employees who work remotely.
ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency is a comprehensive guide to understanding and implementing ERP systems. For a more in-depth look at how ERP can transform your business, check out ERP: Unlocking the Power of Integrated Business Management.
This article provides valuable insights into the benefits and challenges of ERP, helping you make informed decisions for your organization. Returning to ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency, this guide offers a step-by-step approach to ERP implementation, ensuring a successful and efficient transition.
Another major trend in the ERP industry is the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can be used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. This can help businesses to improve their efficiency and productivity.
Finally, the ERP industry is also seeing a growing trend towards mobile-first design. Mobile ERP systems are designed to be used on smartphones and tablets, which makes them ideal for businesses that have employees who are always on the go.
Benefits of Emerging ERP Trends and Innovations
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Increased flexibility and scalability
- Reduced costs
- Improved decision-making
- Enhanced customer service
Case Studies of Successful ERP Implementations
Various businesses have experienced significant improvements after implementing ERP systems. These case studies demonstrate the tangible benefits and positive outcomes organizations can achieve through ERP integration.
One notable example is the implementation of an ERP system by a global manufacturing company. The company faced challenges with disparate systems and inefficient processes, leading to production delays and inventory issues. After implementing an ERP system, the company streamlined its operations, improved communication between departments, and gained real-time visibility into its supply chain.
This resulted in reduced production lead times, optimized inventory levels, and increased customer satisfaction.
Benefits of ERP Integration
- Improved operational efficiency
- Enhanced collaboration and communication
- Increased data accuracy and visibility
- Reduced costs and improved profitability
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
Outcomes Achieved
- Streamlined business processes
- Reduced errors and improved data integrity
- Increased productivity and efficiency
- Improved decision-making based on real-time data
- Enhanced compliance and regulatory adherence
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, ERP Meaning and Definition: The Ultimate Guide to Business Integration and Efficiency has illuminated the path towards harnessing the transformative power of ERP. By understanding its core concepts, benefits, and implementation strategies, you are now equipped to make informed decisions that will propel your business to new heights of efficiency and success.
Embrace the future of business integration and unlock the limitless potential that ERP holds for your organization.
General Inquiries
What are the key benefits of ERP integration?
ERP integration streamlines processes, reduces costs, enhances data accuracy, improves collaboration, and provides real-time insights for better decision-making.
What are the core modules typically found in an ERP system?
Common ERP modules include Finance, Supply Chain Management, Human Resources, Customer Relationship Management, and Manufacturing.
What factors should be considered when selecting an ERP system?
Evaluate factors such as business size, industry requirements, scalability, cost, vendor reputation, and implementation support.
What are the potential challenges of ERP implementation?
Challenges may include data migration, process mapping, user training, change management, and integration with existing systems.
How can businesses overcome ERP implementation challenges?
Overcome challenges through careful planning, vendor collaboration, user involvement, phased implementation, and ongoing support.





