What is the difference between margin and profit? Understanding these two crucial financial metrics is essential for businesses to gauge their financial performance and make informed decisions. This article delves into the definitions, formulas, and key differences between margin and profit, highlighting their impact on overall financial health.
Margin and profit are two distinct yet interconnected concepts that provide valuable insights into a company’s financial standing. Margin measures the percentage of revenue left after deducting variable costs, while profit represents the net income after subtracting all expenses from revenue.
By analyzing both margin and profit, businesses can identify areas for improvement and optimize their financial performance.
Definition of Margin: What Is The Difference Between Margin And Profit?
In the world of business and finance, the term “margin” refers to a calculation that measures the profitability of a company’s operations. It indicates the difference between the revenue generated from sales and the costs incurred to produce and sell those goods or services.
The intricacies of margin and profit analysis can be illuminated by exploring the transformative potential of blockchain technology. Dive into Smart Contracts with Solidity: A Comprehensive Guide to Blockchain Development to unravel the intricacies of decentralized finance and its impact on margin and profit dynamics.
Return to the dissection of margin and profit armed with a deeper understanding of how blockchain innovation is reshaping the financial landscape.
There are several types of margins that businesses use to assess their financial performance, each providing a different perspective on profitability. These include:
Gross Margin
Gross margin measures the profit earned from sales after deducting the direct costs associated with producing the goods or services sold. It is calculated as:
Gross Margin = (Revenue
Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue
A higher gross margin indicates that the business is efficiently managing its production costs and generating a healthy profit from each sale.
Definition of Profit
Profit is a financial measure of a company’s financial performance. It represents the excess of revenues over expenses during a specific period, typically a quarter or a year.
There are different types of profit, each providing insights into a company’s financial health and profitability. The most common types of profit include:
Gross Profit
Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from the revenue generated by sales. It represents the profit earned from the core business operations before considering other expenses.
Operating Profit
Operating profit is calculated by subtracting operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, and utilities, from gross profit. It represents the profit generated from the company’s core operations, excluding non-operating expenses.
Net Profit
Net profit, also known as net income, is calculated by subtracting all expenses, including non-operating expenses such as interest payments and taxes, from the operating profit. It represents the final profit earned by the company after considering all expenses.
Understanding the nuances between margin and profit is crucial in financial management. While margin measures the percentage difference between selling price and cost, profit represents the absolute monetary gain. Delving deeper into the realm of digital assets, the article NFT or Coin: Unraveling the Enigma of Digital Assets explores the intricacies of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and cryptocurrencies, providing insights into their unique characteristics and potential value.
Returning to our initial topic, the distinction between margin and profit remains a fundamental concept in assessing financial performance and making informed investment decisions.
Key Differences between Margin and Profit
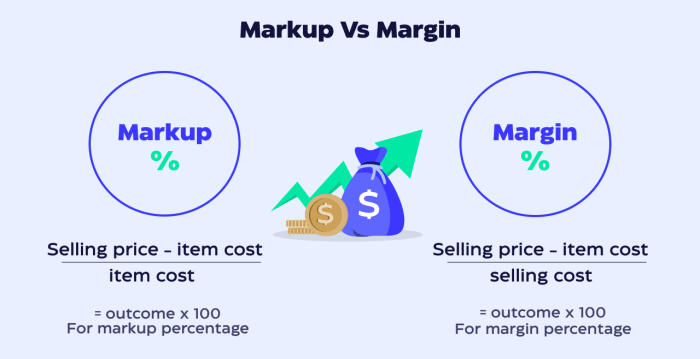
Margin and profit are two crucial financial metrics that measure a company’s financial performance. While they are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct concepts with different formulas and implications. Understanding the key differences between margin and profit is essential for accurate financial analysis and decision-making.
Definition and Formulas
Marginrefers to the percentage of revenue left after deducting expenses. It indicates the profitability of a company’s operations and is calculated as:
Margin = (Revenue
Expenses) / Revenue x 100%
Understanding the difference between margin and profit is crucial for businesses to optimize their financial performance. While margin measures the profitability of each sale, profit represents the overall earnings after deducting expenses. To gain deeper insights into financial management, consider exploring our comprehensive guide on How to Build a Web3 NFT Minting Platform , where you’ll learn about advanced concepts and strategies to enhance your financial acumen and maximize your business’s profitability.
Profit, on the other hand, represents the absolute amount of money earned after subtracting expenses from revenue. It measures the overall financial gain of a company and is calculated as:
Profit = Revenue
Expenses
Key Differences
- Percentage vs. Absolute Value:Margin is expressed as a percentage, while profit is an absolute value in currency units (e.g., dollars or euros).
- Focus:Margin measures the efficiency of a company’s operations, while profit focuses on the overall financial outcome.
- Expense Consideration:Margin considers all expenses, including both fixed and variable costs. Profit, on the other hand, considers only variable costs, as fixed costs are already accounted for in the revenue figure.
- Impact of Sales Volume:Margin is directly influenced by sales volume, as higher sales lead to a higher revenue base and potentially higher margins. Profit, however, can increase with higher sales volume but is not directly proportional to it.
- Decision-Making:Margin is often used to compare the profitability of different products or services within a company. Profit is more relevant for assessing the overall financial health and growth potential of a company.
Impact of Margin on Profit
Profitability is one of the key goals of any business, and margin plays a crucial role in determining overall financial performance. Margin refers to the difference between the selling price of a product or service and its cost of production, while profit represents the actual financial gain from the sale.
Understanding the impact of margin on profit is essential for businesses to optimize their pricing strategies, reduce costs, and maximize earnings.
Margin directly influences the amount of profit a business earns. A higher margin means that a larger portion of the selling price goes towards profit, while a lower margin results in a smaller profit margin. For instance, if a product is sold for $100 and its cost of production is $70, the margin is $30 (or 30%). If the cost of production increases to $80, the margin decreases to $20 (or 20%).
Examples of Improved Margin Leading to Increased Profitability, What is the difference between margin and profit?
- Cost Reduction:Businesses can increase their margin by reducing the cost of production. This can involve negotiating better deals with suppliers, optimizing production processes, or reducing waste.
- Price Optimization:Another way to increase margin is to adjust the selling price of the product or service. However, it’s important to consider market demand and competition when making pricing decisions.
- Product Mix:Businesses can also improve their overall margin by focusing on selling products or services with higher margins. This may involve discontinuing or reducing the production of low-margin items.
In summary, margin has a significant impact on profit and overall financial performance. By understanding the relationship between margin and profit, businesses can make informed decisions to improve their pricing strategies, reduce costs, and maximize earnings.
Understanding the nuances between margin and profit is crucial for any business venture. To further enhance your financial knowledge, consider exploring Learn Solidity: A Comprehensive Guide to Web Development with Solidity . This guide delves into the intricacies of web development using Solidity, empowering you to create robust and efficient web applications.
Returning to our initial topic, understanding the difference between margin and profit remains paramount in evaluating business performance.
Factors Affecting Margin
Margin can be influenced by various factors, making it crucial for businesses to understand and manage these elements to optimize profitability.
Understanding the distinction between margin and profit is crucial in business, especially when considering the booming NFT market. To delve deeper into the intricacies of this topic, refer to our comprehensive guide, Sell NFTs Online: A Comprehensive Guide for Success . This guide provides valuable insights into maximizing profit margins and navigating the NFT landscape effectively.
By exploring this resource, you can gain a clearer understanding of the fundamental concepts of margin and profit, empowering you to make informed decisions in your business ventures.
Key factors that impact margin include:
Revenue
- Sales volume:Higher sales volume leads to increased revenue, potentially boosting margin.
- Pricing strategy:Setting appropriate prices that balance customer demand and profitability is essential.
- Market share:A larger market share allows businesses to negotiate better terms with suppliers and customers, improving margin.
Costs
- Cost of goods sold (COGS):Direct costs associated with producing or acquiring goods or services.
- Operating expenses:Indirect costs related to running the business, such as rent, salaries, and marketing.
- Fixed costs:Costs that remain relatively constant regardless of production or sales volume.
Efficiency
- Operational efficiency:Optimizing processes to reduce waste and improve productivity.
- Supply chain management:Efficiently managing suppliers and logistics to minimize costs.
- Inventory management:Controlling inventory levels to reduce holding costs and avoid spoilage.
Optimizing margin requires businesses to strike a balance between these factors. Strategies may include increasing revenue through sales growth or pricing adjustments, reducing costs through efficiency measures or negotiation, and improving operational efficiency.
Factors Affecting Profit
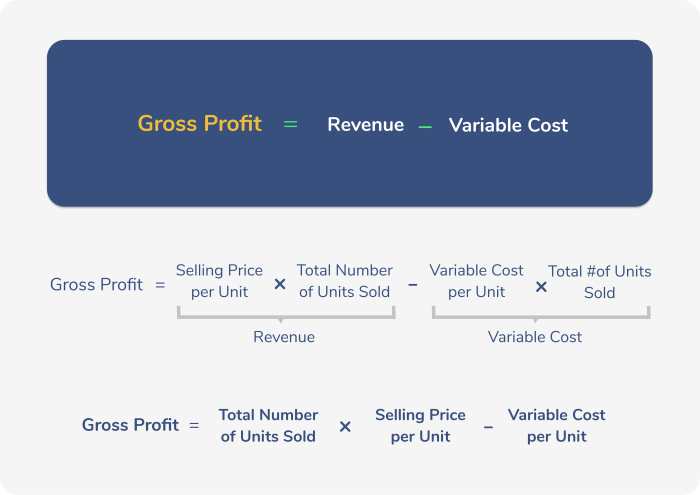
Profit is influenced by various factors that businesses must carefully manage to maximize their financial performance. These factors include revenue, expenses, and taxes.
Revenue
- Revenue refers to the total income generated by a business through the sale of goods or services.
- Factors that affect revenue include product or service demand, pricing strategies, and market competition.
Expenses
- Expenses represent the costs incurred by a business in the process of generating revenue.
- Types of expenses include cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and interest expenses.
- Effective cost management is crucial for minimizing expenses and maximizing profit.
Taxes
- Taxes are mandatory payments made by businesses to government authorities.
- Taxes can significantly impact profit, especially in jurisdictions with high tax rates.
- Businesses should consider tax implications when making decisions that affect their financial performance.
Importance of Margin and Profit Analysis
Analyzing margin and profit is crucial for financial decision-making as these metrics offer valuable insights into a company’s financial health and performance. They help businesses assess their profitability, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to maximize financial outcomes.
Profitability analysis allows companies to evaluate their ability to generate income, while margin analysis provides a deeper understanding of how efficiently they use their resources and generate revenue. By examining these metrics together, businesses can gain a comprehensive view of their financial situation and make informed decisions to improve profitability.
Importance of Margin Analysis
- Identifies areas for cost reduction and efficiency improvements.
- Provides insights into pricing strategies and their impact on profitability.
- Helps in comparing performance with industry benchmarks and competitors.
Importance of Profit Analysis
- Assesses the overall financial performance and ability to generate income.
- Provides a basis for dividend payments and investment decisions.
- Helps in evaluating the company’s growth potential and sustainability.
Margin and Profit in Different Industries

Margin and profit levels can vary significantly across different industries. This is due to a number of factors, including the nature of the industry, the competitive landscape, and the cost structure.
For example, industries with high fixed costs, such as manufacturing, tend to have lower margins than industries with low fixed costs, such as services. This is because fixed costs must be covered even when sales are low, which can eat into profits.
Factors Contributing to Margin and Profit Differences
- Industry structure:Industries with high barriers to entry and few competitors tend to have higher margins than industries with low barriers to entry and many competitors.
- Product differentiation:Industries with products that are highly differentiated from competitors tend to have higher margins than industries with products that are more standardized.
- Cost structure:Industries with high fixed costs tend to have lower margins than industries with low fixed costs.
- Market conditions:Industries that are experiencing high demand and low supply tend to have higher margins than industries that are experiencing low demand and high supply.
Case Study
Improving Margin and Profit: A Success Story
Analyzing the success of a company that has effectively improved its margin and profit can provide valuable insights into the strategies and techniques that drive these improvements.
Strategies and Techniques
The company implemented a comprehensive plan that included:
- Cost optimization:Reducing expenses through process improvements, supplier negotiations, and inventory management.
- Revenue enhancement:Upselling and cross-selling to increase sales volume, introducing new products or services, and expanding into new markets.
- Pricing strategy:Adjusting prices to optimize both margin and sales volume, using data analytics to determine optimal price points.
- Operational efficiency:Streamlining operations to improve productivity, reduce waste, and increase capacity.
- Talent management:Hiring and retaining skilled employees who can contribute to the company’s success.
The combination of these strategies resulted in significant improvements in both margin and profit, leading to increased profitability and financial stability.
Best Practices for Margin and Profit Management
Maintaining optimal margins and profits requires effective management strategies. Here are some best practices to help businesses maximize their profitability:
1. Establish clear margin and profit targets: Set realistic and achievable targets for both margin and profit to guide decision-making and track progress.
2. Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs): Track key metrics such as gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin to identify areas for improvement and ensure alignment with targets.
3. Analyze cost structure: Regularly review and optimize cost structure to identify areas where expenses can be reduced without compromising quality or customer satisfaction.
4. Optimize pricing strategy: Implement pricing strategies that balance customer value with profitability, considering factors such as market demand, competition, and production costs.
5. Manage inventory efficiently: Maintain optimal inventory levels to minimize holding costs and reduce the risk of obsolescence or spoilage, ensuring a healthy cash flow.
6. Improve operational efficiency: Streamline operations to enhance productivity, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency, which can positively impact margins and profits.
7. Invest in technology: Leverage technology to automate tasks, improve data analysis, and enhance decision-making, leading to cost savings and increased profitability.
8. Enhance customer experience: Focus on providing exceptional customer experiences to drive repeat business, positive word-of-mouth, and ultimately higher margins and profits.
Final Conclusion

Understanding the difference between margin and profit empowers businesses to make informed decisions, optimize their financial performance, and achieve long-term success. By carefully monitoring and analyzing these metrics, companies can identify opportunities to increase revenue, reduce costs, and ultimately enhance their profitability.
FAQ Resource
What is the difference between gross margin and net margin?
Gross margin measures the percentage of revenue left after deducting only variable costs, while net margin represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting all expenses, including both variable and fixed costs.
How does margin impact profit?
Higher margins generally lead to higher profits, as a larger percentage of revenue is available to cover fixed costs and generate net income.
What are some factors that can affect margin?
Factors that can impact margin include revenue, variable costs, efficiency, and pricing strategies.
How can businesses improve their profit?
Businesses can improve their profit by increasing revenue, reducing expenses, optimizing margins, and managing costs effectively.





