Eth2 and comparison – As Ethereum 2.0 takes center stage, let’s embark on an enthralling exploration of its innovations, comparing it with its predecessor to unravel the transformative impact it promises. Dive into the intricacies of consensus mechanisms, sharding, scalability, and more, as we dissect the intricacies of this highly anticipated upgrade.
Ethereum 2.0 stands as a beacon of innovation, promising to reshape the blockchain landscape. Join us as we delve into its groundbreaking features, examining how they elevate Ethereum’s capabilities and pave the way for a future of decentralized applications and transformative technologies.
Consensus Mechanism

Ethereum 1.0 relies on Proof-of-Work (PoW), a consensus mechanism that requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. In contrast, Ethereum 2.0 employs Proof-of-Stake (PoS), where validators are chosen based on the amount of ETH they hold to validate transactions and propose new blocks.
Advantages of Proof-of-Work
- Security:PoW is considered more secure than PoS because it requires significant computational power to attack the network.
- Decentralization:PoW allows anyone with the necessary hardware to participate in the mining process, promoting decentralization.
Disadvantages of Proof-of-Work
- Energy consumption:PoW is highly energy-intensive, leading to environmental concerns.
- Scalability:The PoW mechanism limits the number of transactions that can be processed per second, affecting scalability.
Advantages of Proof-of-Stake
- Energy efficiency:PoS is much more energy-efficient than PoW, reducing its environmental impact.
- Scalability:PoS allows for higher transaction throughput and faster block confirmation times.
Disadvantages of Proof-of-Stake
- Security:PoS may be less secure than PoW, as it is vulnerable to attacks from validators who hold a significant portion of the stake.
- Centralization:PoS can lead to centralization, as validators with larger stakes have a higher chance of being selected to validate blocks.
Sharding
Sharding is a key component of Ethereum 2.0 that aims to significantly increase the scalability of the network. It involves dividing the Ethereum blockchain into multiple smaller and more manageable pieces called shards.
Each shard operates independently, processing its own set of transactions and maintaining its own state. This allows for parallel processing, where multiple shards can work on different transactions simultaneously, drastically increasing the overall transaction throughput of the network.
Benefits of Sharding
- Increased Scalability:Sharding enables Ethereum to handle a much larger number of transactions per second, making it more suitable for large-scale applications and enterprise use cases.
- Reduced Congestion:By distributing the workload across multiple shards, sharding helps to reduce network congestion and lower transaction fees.
- Improved Security:Sharding can enhance the security of the Ethereum network by making it more difficult for attackers to compromise the entire blockchain.
Challenges of Sharding
- Cross-Shard Communication:One of the challenges with sharding is ensuring efficient communication between different shards. Transactions that involve multiple shards require coordination and data exchange, which can add complexity to the system.
- State Synchronization:Each shard maintains its own state, which needs to be synchronized with other shards to ensure data consistency. This can introduce delays and increase the computational overhead.
- Data Availability:Sharding can lead to reduced data availability, as not all nodes have access to the complete state of the entire blockchain. This can affect the ability of certain applications to access and verify data.
Scalability: Eth2 And Comparison
Ethereum 1.0 has faced scalability issues due to its proof-of-work consensus mechanism and limited block size. Ethereum 2.0 aims to address these issues through its proof-of-stake consensus mechanism and sharding, which enables parallel transaction processing.
Ethereum 2.0’s proof-of-stake consensus mechanism is more energy-efficient and allows for faster block validation, resulting in higher transaction throughput. Sharding divides the Ethereum network into smaller, parallel chains called shards, each processing a portion of the transactions. This allows Ethereum 2.0 to handle a significantly larger number of transactions than Ethereum 1.0.
Transaction Throughput, Eth2 and comparison
Ethereum 1.0 currently has a transaction throughput of approximately 15 transactions per second (TPS). Ethereum 2.0 is expected to increase this throughput to 100,000 TPS, a significant improvement that will enable the network to handle a much higher volume of transactions.
Latency
Latency refers to the time it takes for a transaction to be confirmed on the network. Ethereum 1.0 has an average latency of around 15 seconds. Ethereum 2.0’s sharding mechanism will reduce latency by allowing transactions to be processed in parallel, resulting in faster confirmation times.
Security
Ethereum 2.0 significantly enhances security compared to Ethereum 1.0 through various mechanisms, such as the implementation of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus, sharding, and a more robust network architecture.
Ethereum 1.0 relies on Proof-of-Work (PoW), which is vulnerable to 51% attacks. In a 51% attack, a malicious actor gains control over a majority of the network’s computing power, allowing them to manipulate transactions and block production. PoS, on the other hand, is less susceptible to 51% attacks as it requires validators to stake their ETH, making it economically infeasible for a single entity to acquire a majority stake.
Sharding
Sharding further enhances security by distributing the network’s workload across multiple shards. This makes it more difficult for attackers to target the entire network, as they would need to compromise multiple shards simultaneously. Additionally, sharding introduces data availability sampling, which allows validators to verify the availability of data across different shards, reducing the risk of data loss or manipulation.
Network Architecture
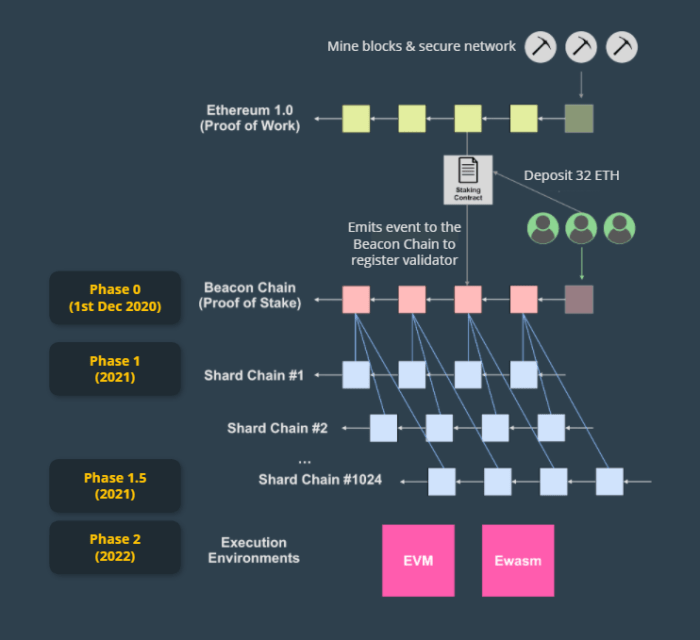
Ethereum 2.0 also features a more robust network architecture with multiple layers of defense. The Beacon Chain, which coordinates the network and manages validator duties, is separate from the shard chains, which process transactions. This separation reduces the risk of a single point of failure and makes it more difficult for attackers to disrupt the network’s operations.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees are a critical aspect of any blockchain network, as they influence the accessibility and usability of the platform. In the case of Ethereum, transaction fees have been a significant concern, particularly during periods of high network congestion.
In Ethereum 1.0, transaction fees are determined by a combination of factors, including network demand, gas price, and gas limit. Gas price represents the amount of ETH a user is willing to pay per unit of gas, while gas limit refers to the maximum amount of gas a user is willing to spend on a transaction.
While eth2 and its comparisons continue to generate buzz in the crypto community, don’t forget about another essential communication tool: WhatsApp. For those who want to master the art of video sharing on this popular platform, WhatsApp Video: The Ultimate Guide to Sharing Like a Pro offers invaluable tips and tricks.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of eth2 and its potential impact, let’s not neglect the importance of effective communication, both in the crypto sphere and beyond.
During periods of high network congestion, gas prices can surge, leading to significantly higher transaction fees.
Ethereum 2.0 Transaction Fees
Ethereum 2.0 aims to address the issue of high transaction fees through several key changes to the network architecture. One significant change is the introduction of sharding, which will divide the Ethereum network into multiple parallel chains, or shards. This will increase the network’s overall capacity and reduce congestion, thereby lowering transaction fees.
Additionally, Ethereum 2.0 will implement a new fee market mechanism known as the “EIP-1559” proposal. This proposal introduces a base fee that is burned rather than going to miners, which helps to stabilize fees and prevent price spikes. The base fee will be adjusted dynamically based on network demand, ensuring that fees remain reasonable even during periods of high congestion.
Eth2, the highly anticipated upgrade to Ethereum, promises to revolutionize the blockchain landscape. To better understand its significance, be sure to check out our in-depth analysis in Eth2 and Comparison: Unlocking Ethereum’ . This comprehensive guide delves into the key differences between Eth1 and Eth2, exploring the implications for scalability, security, and decentralization.
By comparing Eth2 with other leading blockchains, you’ll gain a clear understanding of its unique advantages and potential.
Overall, the changes introduced in Ethereum 2.0 are expected to significantly reduce transaction fees compared to Ethereum 1.0. This will improve the accessibility and usability of the Ethereum network, making it more attractive for a wider range of applications.
Smart Contract Compatibility
Ethereum 2.0 will bring significant changes to the Ethereum network, including a new consensus mechanism and sharding. These changes will have implications for the compatibility of smart contracts between Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0.The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the runtime environment for smart contracts on Ethereum.
The EVM is a stack-based virtual machine that executes bytecode, which is the compiled form of smart contract code. The EVM is designed to be deterministic, meaning that the same bytecode will always produce the same output, regardless of the environment in which it is executed.Ethereum
2.0 will introduce a new EVM, called the eWASM VM. The eWASM VM is based on the WebAssembly (WASM) standard, which is a binary format for portable code. WASM is designed to be more efficient than the EVM, and it is also more secure.The
eWASM VM will not be fully compatible with the EVM. This means that some smart contracts that run on Ethereum 1.0 will not be able to run on Ethereum 2.0 without being recompiled.There are a number of potential challenges associated with migrating smart contracts from Ethereum 1.0 to Ethereum 2.0. One challenge is that the eWASM VM has a different instruction set than the EVM.
This means that smart contract developers will need to recompile their contracts to run on the eWASM VM.Another challenge is that the eWASM VM has a different gas model than the EVM. This means that smart contracts that are designed to run on the EVM may not run efficiently on the eWASM VM.Despite
these challenges, there are a number of strategies that smart contract developers can use to migrate their contracts to Ethereum 2.0. One strategy is to use a transpiler to convert EVM bytecode to eWASM bytecode. Another strategy is to use a shim layer to allow EVM smart contracts to run on the eWASM VM.
Migration Strategies
There are a number of different strategies that smart contract developers can use to migrate their contracts to Ethereum 2.0.One strategy is to use a transpiler to convert EVM bytecode to eWASM bytecode. Transpilers are tools that translate code from one language to another.
Understanding the intricacies of Eth2 and its various comparisons can be a daunting task. For those looking to venture into the world of digital art and collectibles, the guide “Craft Your Own NFT Minting Website: A Comprehensive Guide” provides invaluable insights . By following the detailed steps outlined in this guide, you can create your own platform for minting and trading NFTs, further immersing yourself in the fascinating realm of Eth2 and its potential.
In this case, a transpiler would translate EVM bytecode to eWASM bytecode.Another strategy is to use a shim layer to allow EVM smart contracts to run on the eWASM VM. A shim layer is a piece of software that sits between two other pieces of software and translates between them.
In this case, a shim layer would translate between the EVM and the eWASM VM.Smart contract developers should carefully consider the different migration strategies and choose the one that is best suited to their needs.
ETH2 is an upcoming upgrade to the Ethereum network that promises to improve scalability and security. While the technical details of ETH2 are complex, it’s essentially a way to make Ethereum more efficient and user-friendly. In the meantime, why not spruce up your WhatsApp chats with stylish themes? Check out Revamp Your WhatsApp Chats with Stylish Themes for some inspiration.
And don’t forget to stay tuned for more updates on ETH2 and its potential impact on the crypto landscape.
Development Tools
The development tools available for Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0 differ significantly. Ethereum 1.0 primarily relies on Solidity, a programming language specifically designed for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Ethereum 2.0, on the other hand, introduces new programming languages and frameworks to support its sharding architecture and consensus mechanism.
Programming Languages
Ethereum 1.0 primarily uses Solidity for smart contract development. Solidity is a high-level, object-oriented language that compiles to EVM bytecode. Ethereum 2.0 introduces new programming languages, such as Vyper and Fe, which are designed to be more efficient and secure than Solidity.
In the realm of blockchain development, Ethereum 2.0 (eth2) has sparked discussions about its comparison to other platforms. For those seeking a deeper understanding of the nuances between different blockchain technologies, Solidity vs Solana: A Comprehensive Comparison for Blockchain Developers provides valuable insights.
This comparison delves into the strengths and limitations of Solidity and Solana, empowering developers to make informed decisions when choosing a platform for their projects. As the blockchain landscape continues to evolve, eth2 and comparison remain crucial considerations for developers seeking to navigate its complexities.
Vyper is a Python-like language that emphasizes simplicity and security, while Fe is a Rust-like language that focuses on performance and concurrency.
Frameworks
Ethereum 1.0 has a wide range of frameworks available for developing decentralized applications (dApps). Popular frameworks include Truffle, Hardhat, and OpenZeppelin. These frameworks provide a comprehensive set of tools for writing, testing, and deploying smart contracts. Ethereum 2.0 introduces new frameworks, such as Ethers.js
and web3.js, which are designed to support the sharding architecture and consensus mechanism. These frameworks provide a streamlined interface for interacting with Ethereum 2.0 nodes and smart contracts.
Debugging Tools
Debugging tools are essential for identifying and fixing errors in smart contracts. Ethereum 1.0 has a variety of debugging tools available, including Remix, Etherscan, and Truffle Debugger. These tools allow developers to step through code, inspect variables, and identify potential issues.
Ethereum 2.0 introduces new debugging tools, such as the Beacon Chain Explorer and the Eth2 Debugger, which are designed to support the sharding architecture and consensus mechanism. These tools provide advanced features for debugging sharded chains and consensus protocols.
Ecosystem Impact
Ethereum 2.0 promises significant improvements to the Ethereum ecosystem, potentially leading to a surge in decentralized application (dApp) development and adoption.
Impact on dApps
Faster transaction speeds and lower fees will make dApps more accessible and user-friendly, attracting a broader audience. This can drive innovation and growth within the dApp ecosystem, leading to the development of more complex and sophisticated applications.
Roadmap and Timeline
Ethereum 2.0’s implementation is a complex and ambitious undertaking, and its timeline has been subject to adjustments and revisions. Initially, the project was expected to be completed in 2019, but it has since been pushed back to a more realistic target date.
Current Status
As of 2023, Ethereum 2.0 is still under development, with several key milestones yet to be achieved. The Beacon Chain, which is the foundation of the new consensus mechanism, has been launched, but the full transition to Proof-of-Stake has not yet taken place.
The sharding functionality, which will significantly increase the network’s scalability, is also still in the works.
Potential Delays and Challenges
The development of Ethereum 2.0 is a highly complex endeavor, and there are a number of potential delays and challenges that could arise. These include technical difficulties, security concerns, and the need to coordinate with a large and diverse community of stakeholders.
However, the Ethereum development team is committed to delivering a robust and scalable platform, and they are working diligently to overcome these challenges.
Closing Notes
Ethereum 2.0 emerges as a testament to the relentless pursuit of innovation within the blockchain realm. Its transformative features, from enhanced scalability to robust security, position it as a catalyst for widespread adoption and the realization of the full potential of decentralized technologies.
As the Ethereum ecosystem embraces this next chapter, we eagerly anticipate the transformative impact it will unleash upon the world.
FAQ Resource
What is the key difference between Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0 introduces a shift from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake consensus, enhances scalability through sharding, and optimizes transaction processing for improved efficiency.
How does sharding contribute to Ethereum 2.0’s scalability?
Sharding divides the Ethereum network into smaller, more manageable partitions, enabling parallel transaction processing and significantly increasing throughput.
What are the advantages of Proof-of-Stake over Proof-of-Work?
Proof-of-Stake eliminates the energy-intensive mining process, making Ethereum 2.0 more environmentally friendly and reducing the barrier to entry for network participation.





