ERP System Example: The Ultimate Guide to Transforming Your Business provides a comprehensive exploration of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, their significance, and the transformative power they hold for businesses. Delve into the intricacies of ERP systems, discover their benefits, and embark on a journey towards revolutionizing your business operations.
Introduction
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software solution that integrates various business functions into a unified system. It allows organizations to manage their operations more efficiently and effectively by centralizing data and automating processes. Implementing an ERP system offers numerous benefits, including improved collaboration, increased productivity, reduced costs, enhanced customer service, and better decision-making.
Benefits of ERP Systems
- Improved Collaboration:ERP systems provide a single platform for all departments to access and share information, fostering better communication and collaboration.
- Increased Productivity:By automating tasks and streamlining processes, ERP systems can significantly increase productivity and free up employees for more strategic work.
- Reduced Costs:ERP systems can reduce costs by eliminating duplicate processes, improving inventory management, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Enhanced Customer Service:With centralized customer data and improved communication, ERP systems enable businesses to provide better customer service and respond more quickly to inquiries.
- Better Decision-Making:ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics, allowing managers to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
Types of ERP Systems
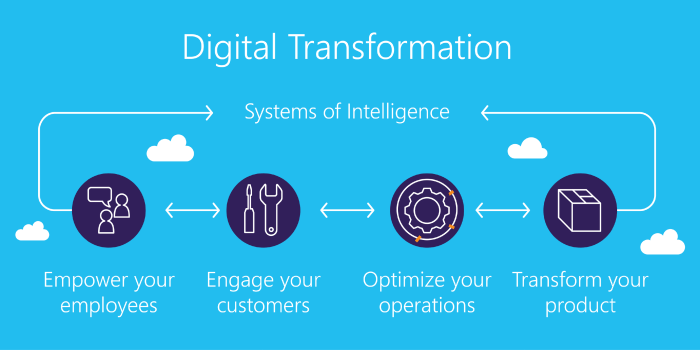
ERP systems come in various types, each designed to meet specific business needs and industries. Understanding the different types of ERP systems is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions when selecting a solution that aligns with their unique requirements.There are two primary types of ERP systems: on-premise and cloud-based.
On-premise ERP systems are installed and managed on the company’s own servers, providing greater control over data and customization. However, they require significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT infrastructure.Cloud-based ERP systems, on the other hand, are hosted by a third-party provider and accessed over the internet.
This eliminates the need for on-site infrastructure and reduces upfront costs. Cloud-based ERP systems offer flexibility, scalability, and access to regular updates and enhancements.In addition to these two main types, ERP systems can also be classified based on their functional scope and industry specialization.
Functional scope refers to the range of business processes covered by the ERP system, such as finance, supply chain management, human resources, and customer relationship management. Industry specialization refers to ERP systems tailored to the specific needs of particular industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, or retail.
Choosing the Right ERP System
Selecting the right ERP system is a crucial step in ensuring a successful implementation. To make an informed decision, consider the following steps and factors:
Step 1: Assess Business Needs
ERP systems are a great way to transform your business, but they can also be complex and expensive. If you’re looking for a more affordable way to get started with ERP, consider using a cloud-based ERP system. Cloud-based ERP systems are typically more affordable than on-premise ERP systems, and they can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
For example, you can even sell your laptop in Dubai using cloud-based ERP systems, as they allow you to manage your business from anywhere in the world. And if you’re looking for a comprehensive guide to ERP systems, be sure to check out “ERP System Example: The Ultimate Guide to Transforming Your Business.”
- Identify specific business processes and challenges that need improvement.
- Determine the functionality and capabilities required to address these needs.
- Consider the size and complexity of your organization and industry.
Step 2: Research and Evaluate Options
- Explore different ERP vendors and their offerings.
- Read reviews, case studies, and industry reports to gather insights.
- Request demos and trial versions to experience the software firsthand.
Step 3: Consider Implementation and Support
- Evaluate the vendor’s implementation experience and methodology.
- Assess the level of support and training provided during and after implementation.
- Consider the availability of customization and integration options.
Step 4: Make a Decision
- Compare the features, functionality, and costs of different systems.
- Consider the long-term value and return on investment.
- Choose the ERP system that best aligns with your business goals and requirements.
Implementing an ERP System
Implementing an ERP system is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. The following steps are typically involved:
- Planning:This phase involves defining the scope of the project, identifying the business requirements, and selecting the right ERP system.
- Data migration:This phase involves transferring data from the old system to the new ERP system.
- Configuration:This phase involves customizing the ERP system to meet the specific needs of the organization.
- Training:This phase involves training users on how to use the new ERP system.
- Go-live:This phase involves launching the new ERP system and making it available to users.
- Post-implementation support:This phase involves providing ongoing support to users after the go-live date.
Challenges of ERP Implementation
There are a number of challenges that can arise during ERP implementation, including:
- Scope creep:This occurs when the scope of the project expands beyond the original plan.
- Data migration issues:These can occur when data is not properly transferred from the old system to the new ERP system.
- Configuration issues:These can occur when the ERP system is not properly configured to meet the specific needs of the organization.
- Training issues:These can occur when users are not properly trained on how to use the new ERP system.
- Resistance to change:This can occur when users are resistant to change and are unwilling to adopt the new ERP system.
Best Practices for ERP Implementation
There are a number of best practices that can help to ensure a successful ERP implementation, including:
- Define a clear scope for the project.
- Identify the business requirements.
- Select the right ERP system.
- Plan for data migration.
- Configure the ERP system to meet the specific needs of the organization.
- Train users on how to use the new ERP system.
- Manage change effectively.
- Provide ongoing support to users after the go-live date.
Integrating ERP with Other Systems
Integrating ERP with other business systems is crucial for streamlining operations and maximizing the benefits of ERP. By connecting ERP with other systems, businesses can automate data flow, eliminate manual processes, and gain a comprehensive view of their operations.
Successful integrations include:
- CRM integration:Connects ERP with customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enabling seamless management of customer data, sales pipelines, and support requests.
- Supply chain management (SCM) integration:Integrates ERP with SCM systems, providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, supplier performance, and logistics.
- Human capital management (HCM) integration:Connects ERP with HCM systems, automating HR processes such as payroll, benefits administration, and employee self-service.
Using an ERP System Effectively
ERP systems can be powerful tools for businesses of all sizes. However, getting the most out of an ERP system requires effective implementation and ongoing use. Here are some tips and best practices to help you use your ERP system effectively:
First, it is important to have a clear understanding of your business needs and how an ERP system can help you meet those needs. This will help you choose the right ERP system and implement it in a way that is tailored to your specific requirements.
User Training and Support
One of the most important factors in successful ERP implementation is user training and support. Users need to be trained on how to use the system effectively and should have access to ongoing support to help them troubleshoot any problems that may arise.
There are a number of different ways to provide user training and support. You can offer formal training classes, provide online documentation, or hire a consultant to help your users get up to speed. The best approach will vary depending on the size and complexity of your organization.
Regardless of the approach you choose, it is important to make sure that your users have the resources they need to use the ERP system effectively. This will help you get the most out of your investment and ensure that your ERP system is a valuable asset to your business.
Case Studies
ERP systems have helped numerous businesses streamline their operations and achieve significant growth. Let’s explore some case studies of companies that have successfully implemented ERP systems.
Benefits of ERP Implementation
* Increased efficiency and productivity
- Improved data accuracy and visibility
- Enhanced customer service
- Reduced operational costs
- Better decision-making
Challenges of ERP Implementation
* High implementation costs
- Complex and time-consuming process
- Potential disruption to business operations
- Resistance to change from employees
Future Trends in ERP Systems
ERP systems are constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. Here are some of the emerging trends that will shape the future of business management:
ERP systems are becoming more cloud-based. This allows businesses to access their ERP system from anywhere, at any time. Cloud-based ERP systems are also more scalable and easier to update than on-premise ERP systems.
ERP systems are becoming more integrated with other business applications. This allows businesses to get a complete view of their operations and make better decisions. For example, ERP systems can be integrated with CRM systems, supply chain management systems, and human capital management systems.
ERP systems are becoming more mobile. This allows businesses to access their ERP system from anywhere, at any time. Mobile ERP systems are also more user-friendly and easier to use than traditional ERP systems.
If you’re looking to enhance your business operations, consider implementing an ERP system. Our comprehensive guide, ERP System Example: The Ultimate Guide to Transforming Your Business, provides valuable insights. Meanwhile, if you’re interested in exploring the lucrative market of Selling Cellphones in Riyadh , our detailed guide offers essential tips and strategies.
Don’t miss out on these resources that can empower your business growth and success.
ERP systems are becoming more intelligent. This allows businesses to automate more tasks and make better decisions. Intelligent ERP systems use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to automate tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and inventory management.
ERP systems are becoming more personalized. This allows businesses to tailor their ERP system to meet their specific needs. Personalized ERP systems can be configured to reflect the unique business processes and workflows of each organization.
The Future of ERP Systems
The future of ERP systems is bright. ERP systems will continue to evolve to meet the changing needs of businesses. As businesses become more global and complex, ERP systems will become even more essential for managing operations and making informed decisions.
Table of ERP System Vendors: ERP System Example: The Ultimate Guide To Transforming Your Business
ERP system vendors offer a wide range of features and pricing options to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes. The following table compares the key features, pricing, and customer reviews of some of the leading ERP system vendors.
It’s important to note that the pricing information provided is subject to change and may vary depending on the specific features and modules required by your business. Additionally, customer reviews can be subjective and may not reflect the experiences of all users.
Vendor Name
- SAP
- Oracle
- Microsoft
- NetSuite
- Epicor
Key Features
- SAP: Comprehensive suite of ERP modules, strong industry expertise, robust reporting and analytics capabilities.
- Oracle: Cloud-based ERP solutions, extensive customization options, integrated CRM and HCM modules.
- Microsoft: Familiar user interface, seamless integration with Microsoft Office products, strong support for small and medium-sized businesses.
- NetSuite: Cloud-based ERP solution designed specifically for small and medium-sized businesses, easy to use and implement.
- Epicor: Industry-specific ERP solutions, strong manufacturing and distribution capabilities, flexible deployment options.
Pricing
- SAP: Pricing varies depending on the specific modules and deployment options selected, typically starts at around $100,000 per year.
- Oracle: Cloud-based pricing starts at around $1,500 per month per user, on-premise pricing varies depending on the modules selected.
- Microsoft: Pricing starts at around $500 per month per user for cloud-based solutions, on-premise pricing varies depending on the modules selected.
- NetSuite: Pricing starts at around $999 per month for cloud-based solutions, with additional costs for add-on modules.
- Epicor: Pricing varies depending on the specific modules and deployment options selected, typically starts at around $50,000 per year.
Customer Reviews
- SAP: Generally positive reviews, praised for its comprehensive functionality and industry expertise, but some users report high implementation costs.
- Oracle: Mixed reviews, praised for its scalability and customization options, but some users report complexity and high maintenance costs.
- Microsoft: Generally positive reviews, praised for its ease of use and integration with Microsoft products, but some users report limited functionality for larger businesses.
- NetSuite: Generally positive reviews, praised for its affordability and ease of implementation, but some users report limited scalability and customization options.
- Epicor: Generally positive reviews, praised for its industry-specific functionality and strong support, but some users report limited reporting and analytics capabilities.
Glossary of ERP Terms

ERP systems are complex software applications, and they come with their own set of terminology. This glossary provides definitions of some of the most common ERP terms and acronyms used in the industry.
Understanding these terms will help you to better understand how ERP systems work and how they can benefit your business.
Acronyms and Abbreviations, ERP System Example: The Ultimate Guide to Transforming Your Business
- ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning
- CRM: Customer Relationship Management
- SCM: Supply Chain Management
- MRP: Material Requirements Planning
- MRP II: Manufacturing Resource Planning
- EDI: Electronic Data Interchange
- WMS: Warehouse Management System
- TMS: Transportation Management System
- BI: Business Intelligence
- ERPaaS: ERP as a Service
Terms
- Business process: A set of activities that are performed in order to achieve a specific business goal.
- Data integration: The process of combining data from different sources into a single, unified view.
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP): A software system that integrates all of the core business processes of an organization, including finance, manufacturing, supply chain management, and human resources.
- Implementation: The process of installing and configuring an ERP system.
- Module: A self-contained software component that performs a specific function within an ERP system.
- Scalability: The ability of an ERP system to handle increased demand without significant performance degradation.
- Software as a service (SaaS): A software delivery model in which software is hosted by a vendor and accessed by customers over the internet.
- System integration: The process of connecting different software systems so that they can share data and functionality.
- User interface: The part of an ERP system that allows users to interact with the software.
- Vendor: A company that sells and supports ERP systems.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, ERP System Example: The Ultimate Guide to Transforming Your Business serves as an invaluable resource for businesses seeking to optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. By embracing the insights and strategies Artikeld in this guide, organizations can unlock the full potential of ERP systems and propel their businesses towards success.
Essential FAQs
What are the key benefits of implementing an ERP system?
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy, enhanced operational efficiency, reduced costs, increased collaboration, and better decision-making.
How do I choose the right ERP system for my business?
Selecting the right ERP system involves considering factors such as your industry, business size, budget, and specific requirements. A step-by-step guide is provided to assist in making an informed decision.
What are the challenges of implementing an ERP system?
Common challenges include data migration, user resistance, and integration with existing systems. However, with careful planning and a phased approach, these challenges can be effectively addressed.





